Transcript from January 11, 2024 podcast
Lucy Stitzer:
Welcome back to Dirt to Dinner’s Digging In podcast.
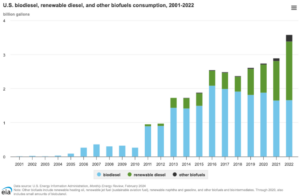
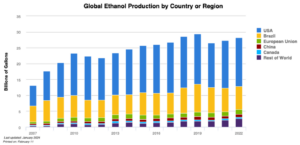
This is Lucy Stitzer and today we’re digging into renewable fuels and the Biden Climate Initiative, which aims to be carbon neutral by 2050. This includes all petroleum that fuels motor vehicles. The standard is to replace the billions of gallons of fuel the United States uses each year with bio with biofuels. Currently, the US uses about 35 billion gallons of ethanol biodiesel, renewable diesel and in limited form sustainable aviation fuel.
Today’s guest is Colin Murphy who is the Deputy Director at the Policy Institute for Energy Environment and the economy at the University of California Davis. In this podcast, he explains the importance of biofuels and how we are going to get to net zero by 2050. Welcome, Colin Murphy.
Colin Murphy:
I am the Deputy Director for the Policy Institute for Energy Environment and Economy at UC Davis and I also co-lead the Low Carbon Fuel Policy Research Initiative. We’re big fans of excessively long wordy titles here at UC Davis, and really what that means, most of my job for the last several years has been to lead our research and engagement efforts around fuel policy.
The main thing we work on is the Low Carbon Fuel standard, which is a policy that was first adopted by California and British Columbia in 2010. Oregon implemented their own in 2016, Washington did theirs last year. So it’s a policy structure that has been very effective in the places that have had it at reducing the amount of petroleum that we consume for transportation. It’s seen as one of the gold-standard fuel policies out there. Certainly not the kind of thing where you’d want it to be the only policy you’re using a transportation, it needs to work with things like electric vehicle policies and policies to switch to renewable electricity and sort of a broad economy-wide portfolio.
But it’s an important part of that portfolio. And so we do research on it. We publish papers like any other academic, but we also spend a lot of our time working with regulators and other policymakers to help understand the topic and help guide them as they make decisions about how they want their jurisdiction to do this. So we have interest from a number of states all over the country who are thinking about, or at some step in the process of adopting a low carbon fuel standard as well as a number of other countries.
Canada just adopted essentially a low carbon fuel standard at the federal level in addition to the one in British Columbia. Brazil has one. It’s limited to liquid fuels only, but they have a very similar policy as well, and a number of other nations are considering it. So yeah, my life for most of the last 10 years has really been largely focused on low carbon fuel standards. But we’re also, we do work on the federal renewable fuel standard, which is a different kind of policy doing increasing amount of work in Europe where they have their own approach to decarbonizing fuels. And we’re really just trying to think about that and make sure we have policy that’s informed by the best science we can.
Lucy Stitzer:
So you’ve been a consultant for the renewable fuel standard for the national one for our country as well as Europe, and then you’re helping Canada and then a variety of different states who are trying to implement their own standards as well?
Colin Murphy:
Yeah, yeah. Not really a consultant so much. We’re an academic research group, so our mission is public benefit and to help also train people. We have grad students coming through and working with us. But yeah, we do research and policy engagement, working with policy makers to help them make good decisions at a wide variety of jurisdictions, mostly in California because it’s obviously where we are and university, it’s California, but we work with jurisdictions all over the world.
Lucy Stitzer:
Well, that’s pretty exciting.
Colin Murphy:
It certainly doesn’t give me a lot of opportunities to be bored.
Lucy Stitzer:
No, I would think not. Well, let’s just talk about the renewable fuel standard and just talk about the United States as a whole in the 2050 green energy, I guess, mandate by Biden indicated that we needed carbon-free electricity by 2035 and carbon free overall by 2050. And so I’m curious about what part biofuels will play in this, and when we think about fuel, I just want to clarify that when I think of fuel, I think we’re talking mostly about cars, trucks, airplanes, and not necessarily to go back on the grid. I think that’s a different subject, but we could certainly talk about what goes back on the grid. But just as far as most of this conversation goes is mostly about, I’ll call it motor fuel, and the UX today uses, yeah, vehicles uses about, I’m thinking, yeah, 135 billion gallons of fuel. And the renewable fuel today is about 37 billion gallons. So am I correct in thinking that there’s just a huge ramp up for the next 25 or so years and to do that?
Colin Murphy:
So there’s definitely going to need to be a huge ramp up, but for most vehicles, so most of that fuel that the US uses is used to fuel on-road vehicles, cars, trucks, buses, stuff like that. And most of it, about 50 or 60%, I’d have to go back and look at the numbers to be sure, is light duty vehicles, passenger cars, cars, trucks, SUVs, things like that.
For the light duty vehicles, battery electric vehicles are almost certainly going to be the main technology that we are using in a world where we have successfully reduced emissions. They have the best combination of low cost, high performance flexibility and everything you need to do that. Very large parts of the medium heavy duty vehicle sector, so these are commercial vehicles, trucks, vans, buses, stuff like that. Most of them can also go onto batteries as well. And in most cases, batteries, because they’re much more efficient at converting energy into motion than an internal combustion engine.
And because they don’t have as many moving parts of an internal combustion engine, their operational costs are a lot lower. So in most cases, it’s actually cheaper. Even today for some vehicle classes, it’s actually cheaper to own and operate an electric vehicle over its full lifespan than it’s internal combustion engine. And batteries are still going to keep getting cheaper over the next 10 years. So most of that 135 billion gallons of fuel is going to be replaced by electricity.
And so we definitely do not have to figure out where we’re going to get 135 billion gallons a year of liquid fuel, which is great because we don’t have the slightest clue where we get 135 billion gallons a year of liquid fuel. So even as important as EVs are, they can’t do everything by themselves. And there’s two real limitations. One is that they’re just some parts of the transportation system where batteries do not have the characteristics to really be a good fit.
The big one is aviation, especially long haul aviation, anything near going more than 500 miles, maybe a thousand miles, batteries just don’t look like they have a trajectory to get to enough energy density where they can satisfy that need. There are also a few specialized applications. Some of the very long haul freight trucks, maybe batteries are not a great fit there. Places people live in really remote areas or really mountainous areas, maybe batteries aren’t the best fit there. So there’s a few other niches of the transportation system besides aircraft that are likely to need something else, probably a liquid fuel for a long time.
Lucy Stitzer:
What about anything on the waterways, barges? They transport a lot of food.
Colin Murphy:
You’re absolutely right. That’s another one where we currently think liquid fuels are likely to be the issue. It’s possible in those hydrogen or renewable natural gas could end up being the fuel there. But for those, yes, liquid fuels may be switching to ammonia or methanol instead of the current kind of heavy oils, or you can make synthetic oils. The thing is waterways, they’re relatively small fraction of the total fuel pool. So even though we definitely have to find a solution for them, it’s not as pressing or scary a problem as is with aviation.
The other thing is with most boats, they have more space and they have looser technical requirements. So with an aircraft, because of the need to be extremely safe with an aircraft and be able to handle a wide range of temperature fluctuations because they fly up very high where it’s pretty cold, the number of potential technical solutions that work in aircraft is a lot more limited than it is in shipping. So while shipping is absolutely something that we have to think of and liquid fuels look like they’re probably going to be the solution there, it’s not, at least to me, not quite as scary or challenging a problem as aircraft.
Lucy Stitzer:
Well, definitely. I mean, your air, you’re in the air and if something goes wrong, there’s
Colin Murphy:
Pull over and wait for someone to bring you another can of gas.
Lucy Stitzer:
Yeah, exactly. And what about trains?
Colin Murphy:
Trains, again, in terms of total magnitude, they’re relatively small. For a lot of trains, you can use electricity and just have a cable overhead or running next to the track. That’s the way a lot of the rail in Europe works is they’re electric and there’s cables running along the track and they get their electricity that way. For trains, hydrogen is a potentially good idea. Hydrogen has a great energy density by mass. So energy for every kilogram of weight is pretty high, but has a lousy energy density by volume.
But with trains, you can put a car full of hydrogen going right behind the train to fuel it to go for thousands of miles, and that doesn’t really affect the train’s functioning all that much. So hydrogen’s one of the ones where I think it’s uniquely well-suited to work in rail applications, possibly maritime, but there’s a little bit more space constraint on the water. So yeah, there’s certainly options there. But again, because the technical requirements are a lot looser than they are for per aircraft, we’re not quite as certain that it has to be a liquid fuel, whereas with aircraft, it’s probably going to have to be a liquid. Right.
Lucy Stitzer:
Yes, I would agree. And then you have the weight and the balance, and as you said, the temperature fluctuation. So there’s a lot with aircraft. So you’ve run through all the different vehicles. So that would bring the 135 billion gallons of fuel that we use today. Would you anticipate that it would come down to fewer, all that? Yeah.
Colin Murphy:
So aircraft, the US consumes about 40 to I think 42, 45, somewhere in their billion gallons a year of jet fuel, excluding military applications. We don’t have great data on that for obvious reasons. With some of the aircraft, like short range lights, 500 miles, maybe a thousand miles probably could go to battery electrics or hydrogen fuel cells. So some of that 40 billion gallons probably could get switched out for or something other than liquid fuel.
But then the needs of shipping, so back of the envelope, probably 40 or 50 billion gallons a year of total demand for liquid fuels over the long run is probably what we’re looking at. And that’s still a lot, but at the very least, it’s not so far out of the realm of what we’ve produced from things other than petroleum that we can at least put together a coherent story about how we might piece together a portfolio that works.
Lucy Stitzer:
So you’re saying we could take out about a hundred or 90 billion out of the petroleum business and we can replace most of that with actually what we’re doing today, our renewable fuel usage is about 37 billion today. And you’re saying we only need about 40? So
Colin Murphy:
Yeah, now from
Lucy Stitzer:
Going to be a big ramp up,
Colin Murphy:
I mean, so of the 37 billion that we’re, yeah, of the 37 billion we’re producing, a lot of that is ethanol, which has a lower energy density. So you have to go and take a few billion gallons off that number to reflect the fact that ethanol is not as energy dense. But yeah, we’re looking at an order of assuming we can take all this fuel and push it to the sectors that need it, that don’t have any other options, doubling the amount may be tripling at most.
There’s a lot of uncertainty here with how quickly is air travel going to keep growing? It’s been the fastest growing form of transportation over the last several decades. So are we going to try to reign in the amount of growth in fuel consumption for air travel or are we going to say no air travel has value. Let’s give people this opportunity to experience the world in a really meaningful and important way.
So we’re going to find a way to make enough fuel to keep supporting, giving more people access to it. And that’s a values question as much as it’s an analytics question. But yeah, we’re looking at something where doubling, probably tripling at most, should be able to give us enough fuel to have a transportation system that provides equal or more total access to mobility than it does today. And the other thing to point out is that there are a number of options for producing liquid fuels that aren’t biofuels.
They’re still kind of in their infancy, but there’s been a lot of interest in a process called electrically derived fuels. And in these, you take electricity, you use the power to break apart carbon dioxide, which you can either capture from the air or capture from an industrial source. We’re going to need a lot of carbon capture under any climate plan that’s going to work, use electricity to break the CO2 apart into carbon monoxide. And then you combine the carbon monoxide with hydrogen, which again you make with electricity using electricity to split water apart into hydrogen and oxygen, combine those together and you can assemble them into liquid fuels using a process called Fischer–Tropsch synthesis. And this is something that’s been done for many decades. It’s not terribly efficient.
Lucy Stitzer:
You can use Fischer–Tropsch for everything. It seems like you could use it for biofuels, you can use it for biodiesel, renewable diesel. I mean, it seems like Fischer–Tropsch is the gold standard for converting any type of matter into a fuel.
Colin Murphy:
Yeah, yeah. I mean the process with biomass is you basically break the biomass down into carbon monoxide and hydrogen and then catalytic assemble those into whatever you want. So as long as you have the carbon and the hydrogen coming from somewhere, you can make a liquid fuel. And in this case, we’re using carbon out of CO2 and hydrogen from water. Previously we’d gotten them out of biomass. The thing is, it’s not terribly efficient.
So right now, if you’re trying to do a fisher to synthesis using this process, you’re losing at least half, sometimes more, like even 60% of the energy you put in to things like waste heat and making unwanted chemicals. The chemical process to synthesize this stuff is not perfectly specific. It makes a lot of different things, only some of which are the molecules you actually want. So we’re pretty confident that we can improve that efficiency somewhat.
We can get the energy losses below 50%, definitely maybe down into the 40% level. And so that at least makes it a lot more tractable for us to be able to make several billion gallons, maybe even 10 or 20 billion gallons a year of liquid fuels out of this Fischer–Tropsch synthesis process. Now, the problem with it is it requires a whole lot of electricity at a time when we are trying to rapidly retire the fossil fuel plants off of our grid because they are what is emitting most of the carbon from the US and from most industrialized economies.
So while we’re trying to go in and retire fossil plants and build enough renewable or other non emitting energy to replace them, if you add on this very large demand to also make a whole bunch of transportation fuel, that really increases the degree of difficulty in terms of getting the electrical grid in turned over. So eels are one of the things where they have the best argument for being a large scale supply of very low carbon fuels in the 2040s probably.
But for the next 10 years, while we’re still getting so much of our electricity off of fossil fuels, it doesn’t really make any sense to burn fossil fuels and then use it to make an EFU when you’re losing half the energy to waste or useless byproducts. So there’s sort of a technology where we need to deploy a few of these facilities at commercial scale in order to start letting the technology mature to get experience with it and to figure out how we’re going to make it more efficient, but it’s not going to be able to provide us a lot of really significant volume at the carbon tendencies. We need until probably at least 10 more like 15 years from now.
Lucy Stitzer:
So like the Fischer–Tropsch technology, we have 2.0.
Colin Murphy:
Yeah, exactly. Yeah. I mean, it has been used in many cases for many decades, but the problem has always been it hasn’t been very efficient. And part of the low efficiency is that lack of selectivity that it makes a lot of different chemicals and not always the ones that you’re looking for or ones that are particularly useful. It’s the kind of problem that humans are usually reasonably good at solving. We’re good at optimizing technological systems, but you have to go and build it to full scale and give people years of experience running these things to figure out, oh, if I tweak this thing here and add a little heat exchanger there or change the chemical composition in this other place, then I can keep incrementally improving the efficiency. So it’s this weird spot where we need to build a few of these facilities at full commercial scale to have that opportunity, but we also need to be careful not to sort of too much of it in the short term because it’s not going to have a very good carbon intensity for a number of years until the grid is much, much cleaner.
Lucy Stitzer:
Really, the biofield market is going to continue to ramp up until 2035, maybe 2040 until we get and solve some of these issues and then also Fischer–Tropsch. And so we really still need corn and soybeans for the next foreseeable future.
Colin Murphy:
So I think that’s the most likely outcome as well. So most of the volume of biofuels used in the US has been determined and driven by the federal policy, the renewable fuel standard, certainly all the corn ethanol, the amount of corn ethanol that the US makes is essentially the amount of corn ethanol that the RFS incentivizes. They don’t go much beyond that level. And the same thing has largely happened with the soybean based diesel substitutes that are growing pretty rapidly right now. And the industry is asking the government to keep expanding the size of the RFS to let them continue growing.
And if you look at the targets that the EPA put out earlier this year, it looks like they’re starting to say it might be time to tap the brakes and not continue this level of growth because they recognize the potential problems that you get into, particularly with land competition as you get to two larger and larger amounts of biofuels.
But the issue is that for both corn and soybeans, biofuels are only part of what they make. So you have about 15 billion gallons a year right now of corn ethanol that’s being produced, and the corn that goes into an ethanol refinery, what the ethanol refinery does, it takes the starch out and makes ethanol out of the starch. But all of the protein, the fiber, most of the other nutrients, and even some of the starch doesn’t convert. Everything gets left behind and gets sold as annual feed called distiller greens.
Most of what would happen, what would’ve happened to that corn if it hadn’t been used for ethanol is it would’ve gone to the animal feed market anyway. So you lose the starch part of the ethanol and that no longer goes to feed the animals. But all of the yeast that ferment the ethanol and grow in the starch, the sort of spend yeast gets added into this diller grain. So you take this corn that would’ve gone a hundred percent annual feed, and instead you have kind of a slightly smaller volume of a higher protein version of animal feed.
All this is to say, at least in the case of corn, we make 15 billion gallons of ethanol. I think it uses about 30% of our corn crop, but it’s not like that 30% of the corn crop goes away, that 30% of the corn crop is still going into annual feed and not having a terribly large impact on the net acreage not a zero impact. It absolutely does have zero impact, and it does cause some land exchange, but it’s not like that 30% is gone and completely out of the food system just comes into the food system in a different way.
Lucy Stitzer:
So I think if you could just explain the four different types just so people can understand what we’re talking about a little bit.
Colin Murphy:
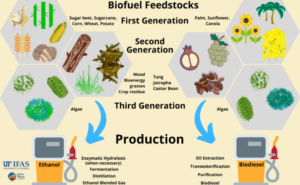
So like you said, ethanol’s kind of the simple one. The way we predominantly make it now is we pull starch out of something in the US it’s pretty much all corn in Brazil or other countries that have a sugar cane industry. The sugar cane is another great way to make ethanol. And then you ferment, you break starch down into sugars, and then you ferment the sugars into alcohols. Essentially the same process you make used for making beer, wine, or spirits just done on an industrial scale. And it wouldn’t taste very good if you tried to drink it directly. And ethanol is currently in the US blended into all gasoline at about a 10% level. That’s what we’ve been doing since the mid two thousands. The having some ethanol gasoline helps the gasoline burn cleaner. You need about six or 7% to really get that clean burning, the oxygen effect.
Beyond that, you’re just trying to reduce the amount of petroleum you use and replace with something that’s lower carbon than petroleum. And there has been a lot of controversy over corn ethanol, whether it is actually lower carbon. There was a very famous study that came out last year, guy named Tyler Lark was the lead author on it, and he made the argument that the RFS was actually ultimately worse, made the corn ethanol worse than petroleum. So I don’t think his methods were quite right. Part of it. The problem with biofuels is a lot of the impact and a lot of greenhouse stuff comes from what we call indirect land use change. And this is where because you have fuel producers now starting to consume agricultural products that historically has only gone into feeding people or animals or a really small number of other industrial uses.
Now the demand for these industrial, these agricultural commodities goes up and somewhere someone in the world is going to have to make more of the stuff to replace what went into fuels. And some of that replacement comes from plowing more land and bringing more land into cultivation. And there’s a big carbon impact from plowing more land. So the LARC paper said because of I luck, the renewable fuel standard and the corn ethanol was worse than the petroleum, there has been a lot of back and forth, there’s several back and forth in terms of open comment letters published by various groups of researchers on that topic. So a lot of methodological uncertainty over that. Beyond that, even if you believe the LARC paper, I think the appropriate take home message from it is maybe we shouldn’t have gone from 15 billion gallons of ethanol we did. And you can’t really unring that bell, even if you sort of stopped and said, well, any land that was cleared, we’ll return to natural form, the carbon’s lost and takes many decades to recover.
And we don’t have that sort of time. So the question I think now is what’s most useful? What’s the way to get the best use out of it? So the other thing with ethanol is there’s a process that some companies have been developed and are looking to commercialize right now where you can convert ethanol into aviation fuel. It’s not entirely unlike the Fischer–Tropsch synthesis we discussed earlier. And it’s small molecule, I’m sorry, it’s a small molecule that you can catalytic assemble into other bigger molecules like the ones that we used to fly planes on. So that might be one of the ways eventually as more EVs take over the on-road space, there’s not going to enough gasoline to blend the ethanol into, and there is some opportunity for us to increase the amount of ethanol we use. Most cars are on road, they can handle 15% ethanol without any problem.
And that would be a way to, again, push petroleum out of the system quicker, or you could turn the ethanol into jet fuel and use it to push petroleum out system that way. And that’s some of the stuff that we’re researching right now for the diesel substitutes. There’s biodiesel and renewable diesel. So biodiesel is made by a process called fatty acid methyl ester, or it’s a relatively simple low energy process to convert. Vegetable oils could be used cooking oil, could be soybean oil or any vegetable oil. You sort of heat it to a medium temperature, add some chemicals, and you can convert it to this biodiesel biodiesel. You can run it into written into most existing diesel engines up to about 20%. If you go over that, you have to start modifying the engine a bit to handle it. Plus, in cold weather, biodiesel starts to, just like most vegetable oils will start to get kind of thick and sludgy and gel up.
So most of the time, biodiesel is blended into regular diesel at a 5% or 7% level, and it’s fine. Doesn’t really cause a lot of problems that way. But because of these infrastructure issues, because of the cold weather performance and the need to only blend to a certain level, it’s not really what people are focused on right now. There’s not a lot of growth in the biodiesel space. Most producers have turned to renewable diesel. They can add some more hydrogen, and if they add a bit more hydrogen, you get a bit more of a coming out like SAF or jet fuel. So you can sort of choose whether you’re going to emphasize the production of renewable diesel or emphasize the production of SAF of renewable jet fuel. To date, most of the policies in the US have made it more beneficial for them to make renewable diesel. So that’s what they do. But with the SAF tax credit under the IRA, it’s likely we’re going to see a lot of the producers starting to tweak their process a bit to push more of their total product out through the SaaS pathways and a little bit less through the diesel pathways. Right.
Lucy Stitzer:
Well, plus the airlines have committed to a higher SAAF percentage.
Colin Murphy:
In the US it’s mostly voluntary commitments and incentives. The Saban challenge, which was the target that was put forth by the Biden administration but didn’t have a whole lot of regulatory teeth behind it, at least not yet, but there’s the SAAF tax credit that’s actually going to make a pretty big difference. Now, there’s a lot of controversy, surprisingly enough in this space controversy around the SAF tax credit and how exactly you’re going to define it. Most of that, again, comes down to this indirect land use change issue. So the way that the tax credit was set forth by Congress was if you’ll have to be at least 50% cleaner than petroleum and you get an additional bonus for every percentage point below 50, they’re able to get. So if you make it even cleaner, you get a larger and larger per gallon incentive.
Lucy Stitzer:
So you go around $1.25. The issue with that is to determine whether you get $1.25 or $1.50 or $1.75 is don’t you have to go back to the farm to determine how they’re growing the corn and determine what type of agriculture they’re using, whether they’re using cover crops or not. And that bodes a whole other series of questions of how do you verify how much carbon they’re sequestering through their growing methods.
Colin Murphy:
That is a big part of it. So we have good tools in the field of lifecycle analysis to understand how much fertilizer and how much diesel and how much electricity is used. For every ton of corn that comes off the field, it’s a lot more complex to understand how the use of a cover crop would affect soil carbon. We know with very high confidence that you can improve the amount of solid carbon retained in the soil by using things like cover crops or compost or possibly biochar or changing the types of crops or the harvest patterns or tilling the soil less. We know there’s a lot of things that can improve it, but soil is a really complex and dynamic system. So knowing that at least pushing that certain things move the needle in the correct direction is one thing, but being able to quantify it and say how many tons per acre are actually being saved?
There is another level of complexity altogether. And then on soil carbon, you also have the issue of permanence. So a farmer can make choices to use cover crops or use compost or switch to no-till agriculture and build up a lot of solid carbon in their soil. But if in five years or 10 years they decide to switch and need to start tilling the soil again, that carbon goes away. And if they received incentives to build up carbon and then in the future they till it and they lose it, all that money is kind of wasted. What they’re being paid for is permanent sequestration of carbon, and it’s not permanent at that point. Or if they sell their land to somebody else, then whoever else has it in the future, they could do the tillage and lose it. So this permanence or reversion risk is one of the things that really makes a lot of the regenerative agriculture policies, incentives so complex on top of the fact that there’s still a lot of uncertainty, and we’re still not able to effectively quantify it without doing a lot of really expensive and time consuming measurement that is probably just too expensive to really allow the farmer to receive much of an incentive, enough incentive for them to want to change their behavior.
So it’s the kind of thing we’re working on, and I think that we’ll keep getting better at it, but there’s a lot of uncertainty around soil carbon. The other big issue is that indirect land use change. The thing with indirect land use change is there’s really no way to develop a sensor that can measure it directly. Because what happens is because somebody is using more soybean oil in the US to make renewable diesel or saf, somebody else in the world might be slashing and burning rainforest in Southeast Asia to do a palm plantation, to grow palm oil, to sell to somebody on their side of the world because the lack of soybean oil coming out of the US has now changed international commodity flows. So there’s really no way for us to very precisely know how much indirect land use change every ton of soybean oil causes.
The only way you can really try to quantify it is through a model. What our models, the uncertainty is very large, and there’s a bunch of places in the model where you have to make these assumptions that are ultimately they’re subjective. There’s no objectively right or wrong way to make it. There’s only a bunch of different subjective ways. For example, when you go soybeans, you get soybean oil and soybean meal. We know how much fertilizer it took to grow the soybeans, so we know how many tons of carbon or grams of carbon were emitted in order to produce this ton of soybeans. But how much of that carbon is the responsibility of the soybean meal versus how much of it is the responsibility of the soybean oil? There’s a lot of different ways to do that. You can look at the mass, you can look at the energy content, you can look at the economic value.
None of them are objectively right or wrong, but they’ll all give you very different answers. And so that’s one of the problems with the model and with modeling eye luck, it’s the only way to assess indirect land use change, but you’re never going to get one definitively correct answer out of it. And so what’s happening with the SAF tax credit is a lot of the producers are asking the Department of Treasury, the ones that have to make the decision because a tax credit, and they’re obviously, they’re not biofuel analysts by nature at Department of Treasury, but they’re asking treasury, okay, well, let’s use this one particular model. And the US uses this model called greet to do lifecycle analysis. It is this fantastically complex model that’s been being developed for 20 years now, and it’s dozens of papers behind it. But in the current version of Greek, they include one IUC estimate based off of a different model.
And this estimate happens to be extremely friendly towards things like corn and soybeans. And so the industry’s saying, well, look, Greek’s the gold standard. This is the thing that they’ve decided to put in for their best guess. So let’s just use that and use that model with that estimate of eye look in order to determine whether we are 50% cleaner than petroleum, and if we are how much far below to figure out the per gallon range. Whereas a lot of other environmental saying, well know you don’t want to use one model. You have to use multiple models and look at the average or look at the range of options that comes out when you make these subjective decisions in different ways. That gives you a better sense of what the actual impact is not to use one of them. And if you do that, then in more justified and reasonable and certainly risk averse way than a lot of the soybean oil fuels or the corn ethanol alcohol to jet fuels wouldn’t be eligible for these credits.
I also recently gave a talk and published a blog post, which is available through our website if you go to lowcarbonfuel.uc.edu under presentations. I gave a talk over the summer talking about this and sort of why you can’t trust any one single model and why you have to go and look at the ensemble of various approaches out there. And even looking at going through the, if we know that we’re, whatever number we pick is probably not going to be right or it’s going to be too high or too low, we need to think about the risks of whether it’s better to overshoot our IUC estimate or to undershoot our ILAC estimate. And when you start thinking through all the various risk factors, it is much, much safer for us to overestimate IUC to take conservative approach and consume maybe less biofuels than would be theoretically optimal because it keeps us away from the more scary and irreversible risks than to error on the other side. So is there a
Lucy Stitzer:
Chance then that the US farmers or any farmer won’t be able to qualify then for selling their corn into the ethanol market?
Colin Murphy:
Well, no, this wouldn’t change the RFS, so this is just whether there would be the option to get an additional credit for producing jet fuel. But yeah, the existing markets aren’t going to change. They’re going to continue the trajectory set by the RFS volume.
Lucy Stitzer:
This is just for SAF, this is, so there’s a possibility then that us farmers wouldn’t be able to sell into the a f market, the ethanol market, but they could sell into the regular ethanol market.
Colin Murphy:
Yeah, that would be it. And so I think the worry is if you adopt too lax of a policy and bring too many biofuels in the system, then you could really start getting a lot of land conversion. And I don’t think there’s necessarily a problem from the food versus fuel standpoint. I mean, that would increase food prices, but probably not a huge amount. It’s more the carbon impact that if we’re going to go and expand agriculture a lot, there’s a huge carbon impact from doing that. You have to do it to feed people. Okay. Feeding people is obviously a priority. We need to do that. So if we have to have some carbon impact and expand land to keep feeding people, that’s one thing. But if we shouldn’t be doing things that have huge carbon impact in the name of, reduce the amount of carbon in the atmosphere, which is really the goal of these biofuel policies. So that’s where we’re sort of getting hung up on, and we’re waiting for treasury to make the decision and see what they ultimately do. But if they choose to take the really lax approach on I luck and let these incentives be given out to a lot of farmers, there’s a chance you could get enough total growth here that you’ll start converting a lot of land globally and the carbon benefits could be pretty bad or they wouldn’t be a benefit at that point.
Lucy Stitzer:
Right. As it pertain to the land use.
Colin Murphy:
Yeah.
Lucy Stitzer:
Portion of the conversation. So let’s circle back to the original actually purpose of this conversation is really, as we do increase renewable fuels with all the ones that we’ve talked about, is there enough land and will there be a food versus fuel debate, putting aside the land use changes and putting aside the regulations and the great standards and all of that, just is there enough land and will there be enough food?
Colin Murphy:
So absolutely there’s enough land. Like we just said before, we jumped ahead a little bit. But the worry here is that we will be producing more corn and soybeans than would be good for the climate. And again, if we have to produce it to feed people, yes, that’s the choice we make, and that’s the right choice. But yeah, so we’re not worried that there’s going to be an absolute lack of land, nor really an absolute lack of food in any way. Are there risks that biofuel policy could increase the price of food? Yes, there are to date, outside of a couple of transient spikes, often around the drought we had in the early 20 teens, we haven’t seen a really massive increase in food prices as a result of fuel policy. It is definitely there, but in a lot of cases, having alternative supplies of fuel means you are less vulnerable to price fluctuations in petroleum.
So yes, there is some increase in the inflation applied to food prices, but less inflation applied to gasoline prices. I’m not enough of an economist to have a really well-informed opinion on the whole, is it better or worse than not having a biofuel policy? But nothing I’ve seen makes us seem like it’s terribly bad. Beyond that, we know that climate change is going to be incredibly bad for a lot of things, including for the food production system because many, many parts of the world that are highly fertile right now won’t be due to higher temperatures and changing rainfall patterns. So as long as the fuels that we’re making are actually lower carbon than the petroleum, they’re displacing. And that has not always been the case. There’s absolutely been several examples where we produce large amounts of fuels that are worse than the petroleum displaced, but many of them are at least lower carbon. And as long as that’s the case, then the value of reducing greenhouse gas emissions probably does more to help secure the long-term food supply from the effects of climate change than it does to hurt it.
Lucy Stitzer:
So it’s not like we’re only growing corn and soybeans only for fuel.
Colin Murphy:
Yes, absolutely. And that’s part of the reason why it’s so hard to analyze the greenhouse gas impacts of biofuels because almost every input has that dual purpose. And so one of the other things that we’ve been seeing is because we had a biofuel policy through the RFF that really until the last five years or so was almost entirely ethanol, really, renewable diesel wasn’t a big thing until five, six years ago because of this policy. We were actually starting to see more growers in the Midwest go from rotations where they do alternate corn and soy every other year, and soy helps add nitrogen because of nitrogen fixing plants. And then also by having different species of plant, you sort of provide a bit of a break in the pathogen cycles, so you need maybe a little bit less herbicide or less additives to controlled diseases for a while.
We’re starting to see more growers going from corn soil rotation to continuous corn because you had this demand for corn biofuels. Well, now with renewable diesel coming online and demanding a lot of soybean oil because that’s the cheapest oil that you can grow really in the western hemisphere, you’re now seeing people go back to corn soy rotations, and that has some additional benefits in terms of slightly reducing the amount of nitrogen fertilizer they need, and slightly reducing the amount of herbicides and other pathogen, chemical pathogen control measures that they have to use. These are, I’m sure, likely to be much smaller than just the big impacts of are these fuels, in fact clean up the petroleum? But they do make a difference. And so the fact that we’re seeing soy growth, there’s some benefits in terms of agronomy there.
Lucy Stitzer:
Well, thank you very much. This has been fascinating and certainly provides a lot of clarity around the renewable fuels conversation.
Colin Murphy:
Yeah, certainly. Happy to help. This is a really complex topic and one that’s going to become increasingly important in the next few years. So very happy to help you and your listeners start to learn more about it. And again, there’s a lot of data and resources available at our website at low carbon fuel dot uc davis.edu.
Lucy Stitzer:
Great. Well, thank you very much.
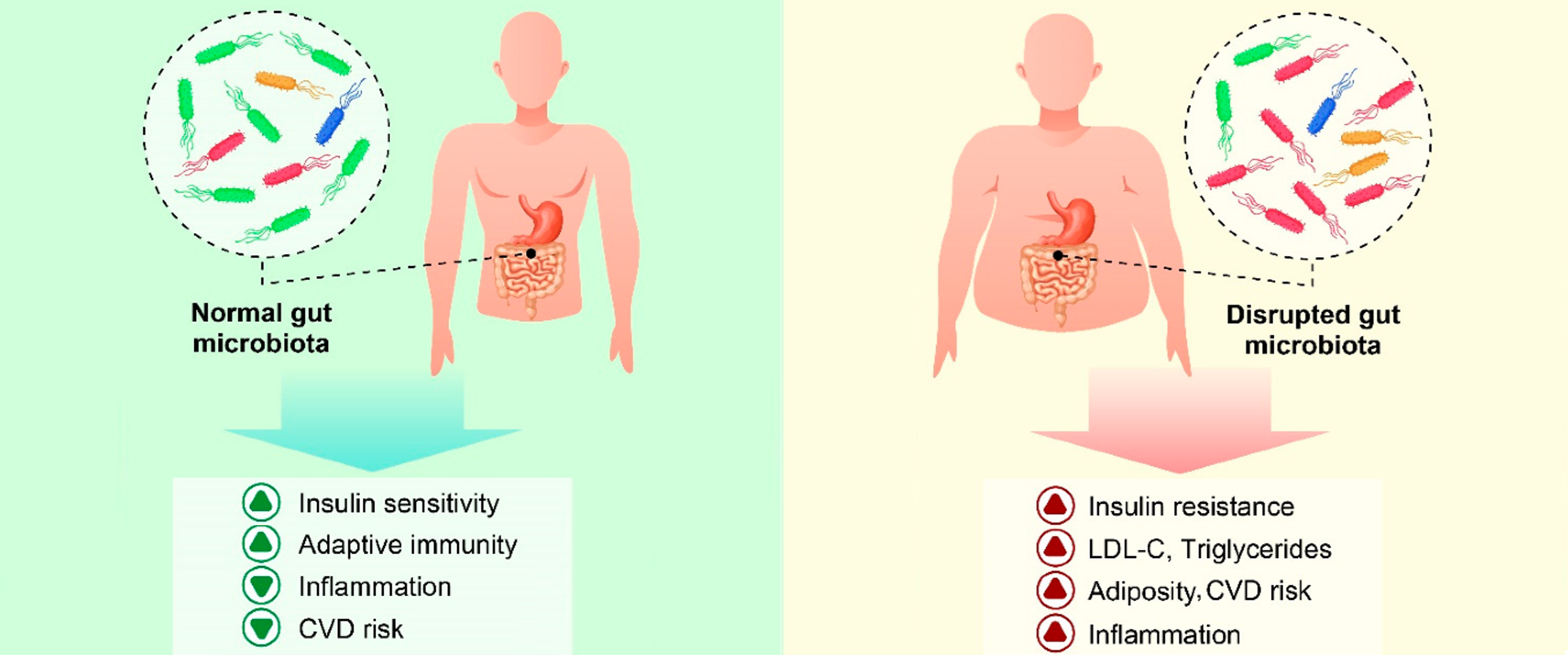
 But many of us may be accidentally sending our hormones the wrong instructions. According to the CDC, over 1 in 3 American adults are already insulin resistant — many without knowing it.
But many of us may be accidentally sending our hormones the wrong instructions. According to the CDC, over 1 in 3 American adults are already insulin resistant — many without knowing it. Produced by the pancreas, it responds to carbohydrates by clearing sugar from the blood and directing it to be stored or used for energy.
Produced by the pancreas, it responds to carbohydrates by clearing sugar from the blood and directing it to be stored or used for energy.If you’re worried you might be negatively impacting your hormonal health via your diet, consider the below, and if you check two or more or these, your body might be sending you warning signals that your diet isn’t giving it clear instructions:



 “
“

 Advocates claim it reduces inflammation, improves mental clarity, and helps manage glucose levels, and promotes weight loss. However, the reported benefits of this diet are more anecdotal than clinical. In fact, multiple studies cite the dangers of this diet, including
Advocates claim it reduces inflammation, improves mental clarity, and helps manage glucose levels, and promotes weight loss. However, the reported benefits of this diet are more anecdotal than clinical. In fact, multiple studies cite the dangers of this diet, including 
 For instance, high consumption of saturated fats like beef tallow – which
For instance, high consumption of saturated fats like beef tallow – which  Yes, ACV can slightly
Yes, ACV can slightly  Experts generally agree that most people, especially women and older adults,
Experts generally agree that most people, especially women and older adults, 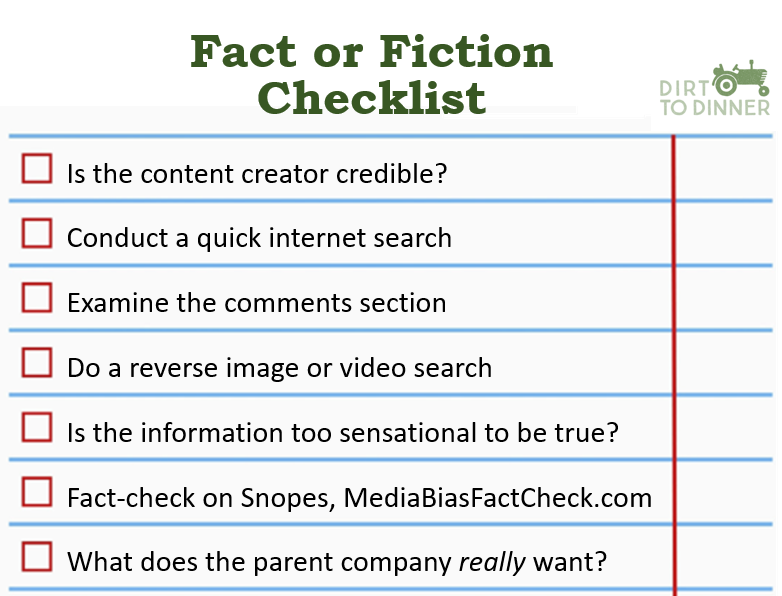

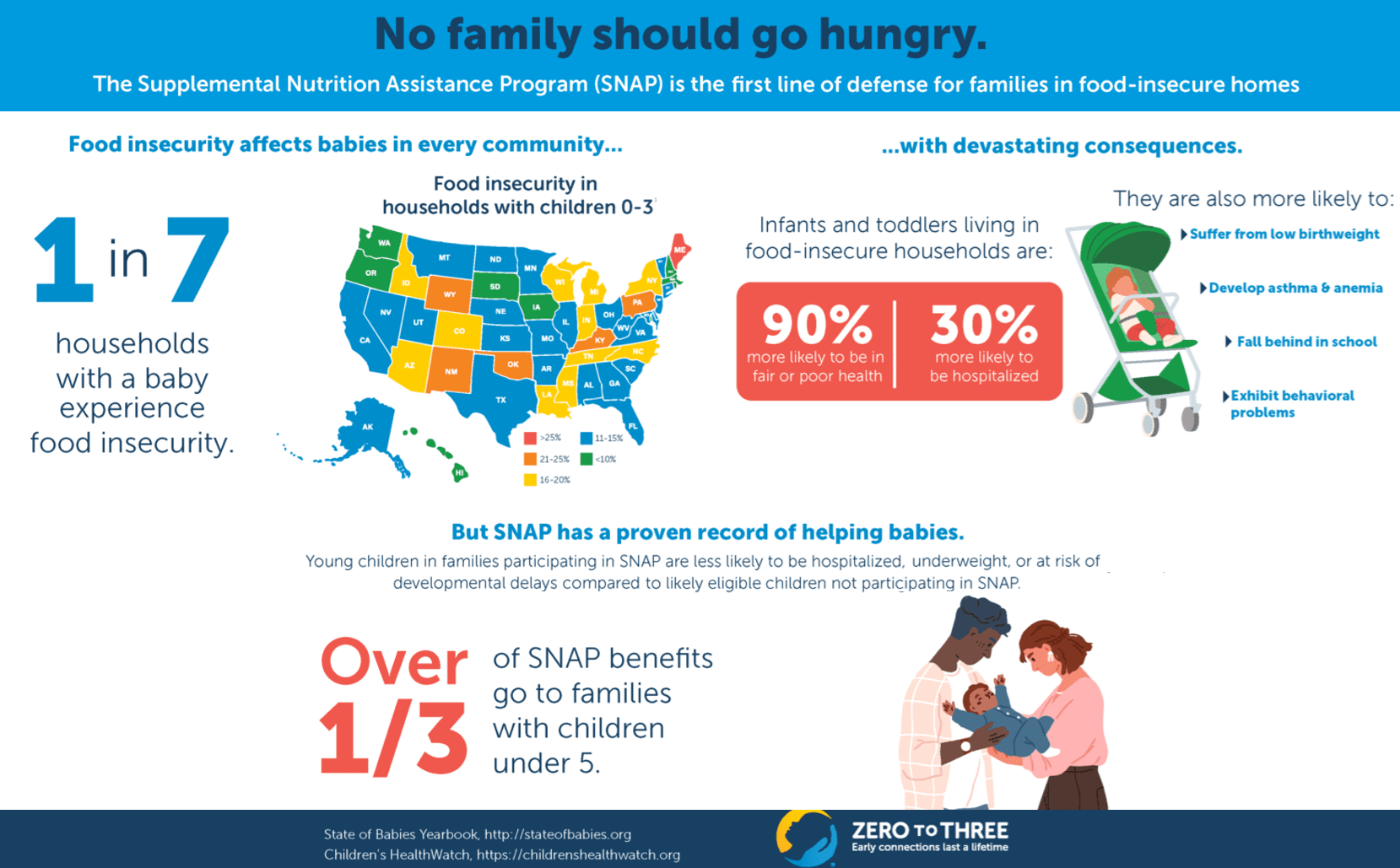
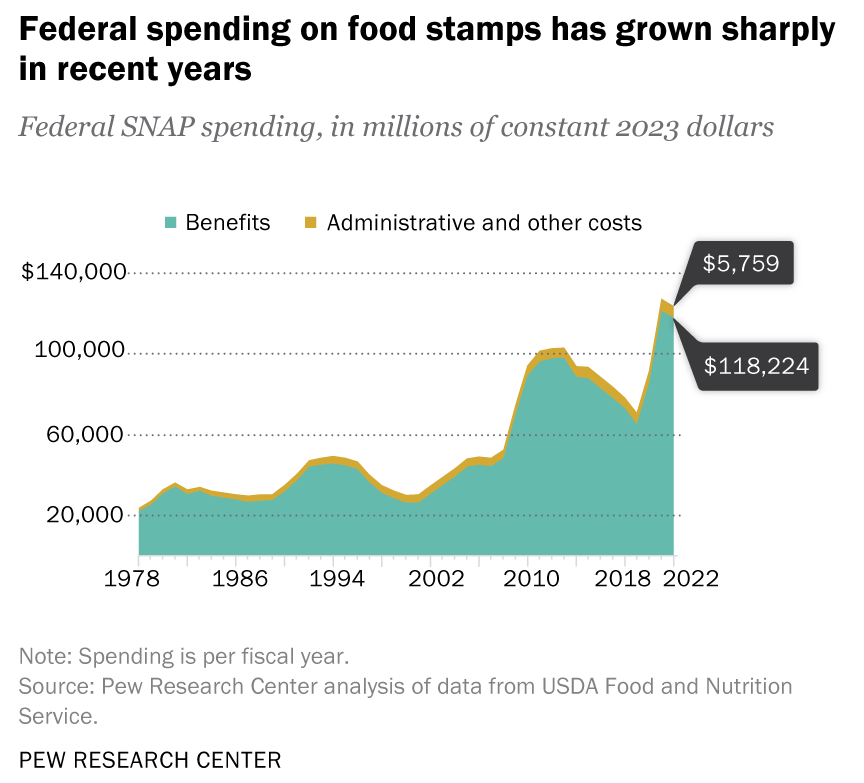
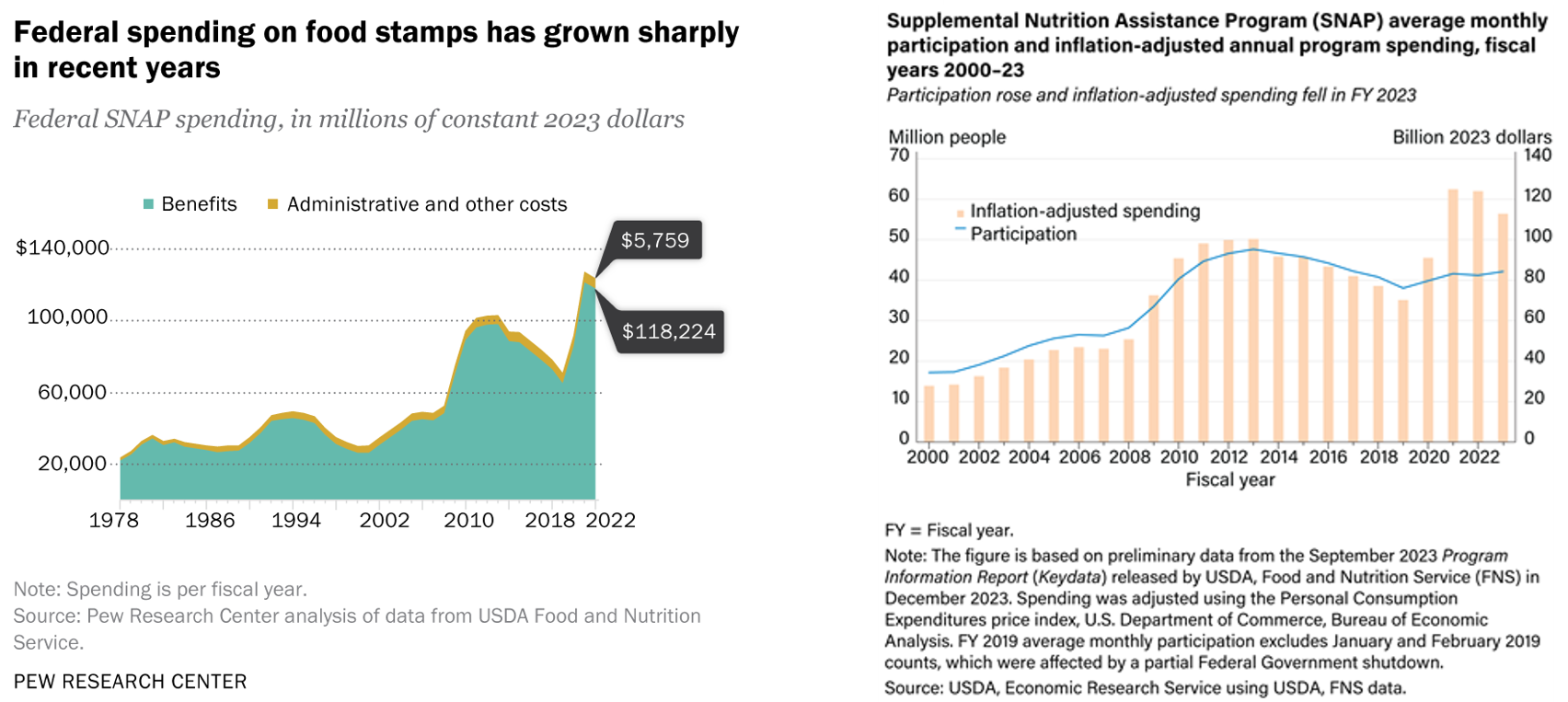
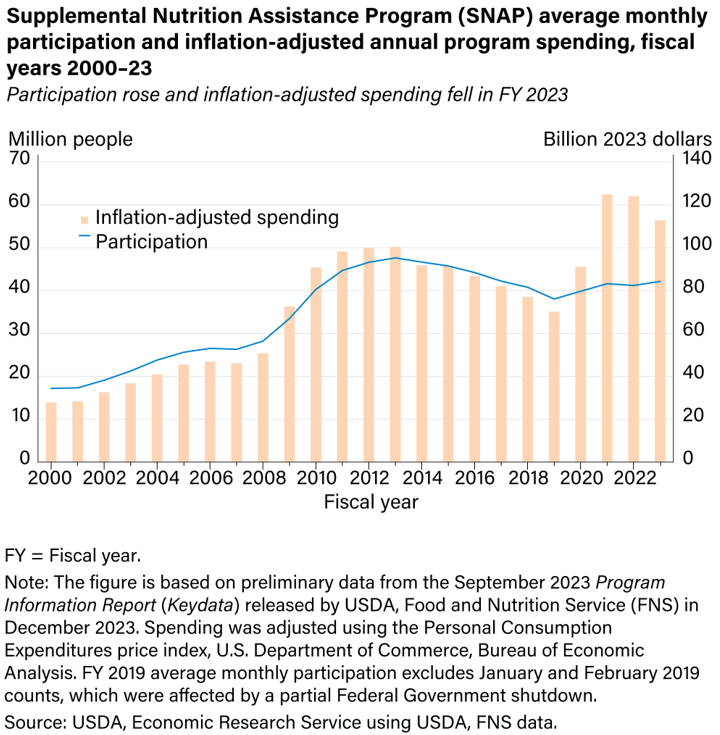 Eligibility and the amount of assistance from SNAP are based on gross and net monthly income. In most cases,
Eligibility and the amount of assistance from SNAP are based on gross and net monthly income. In most cases, 
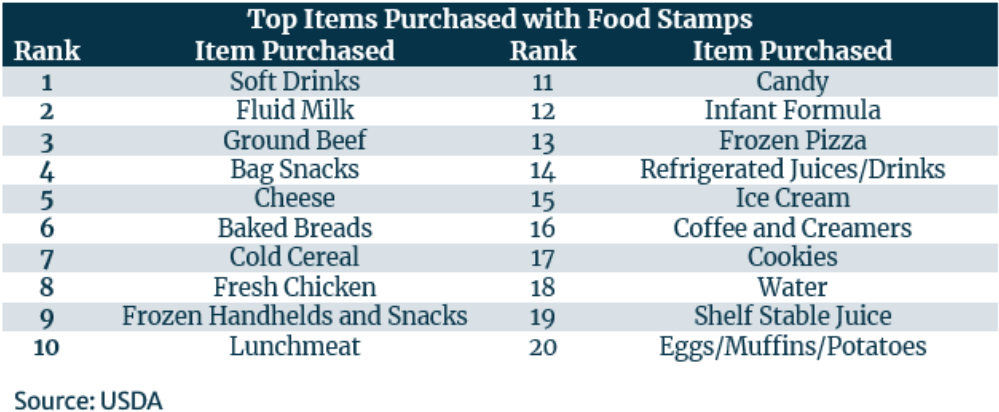

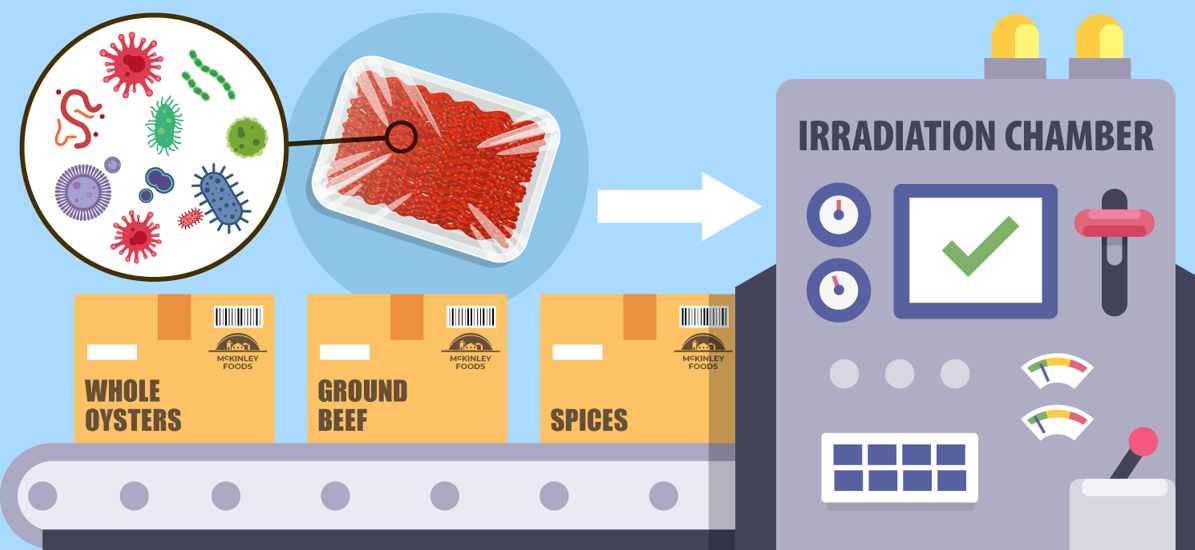
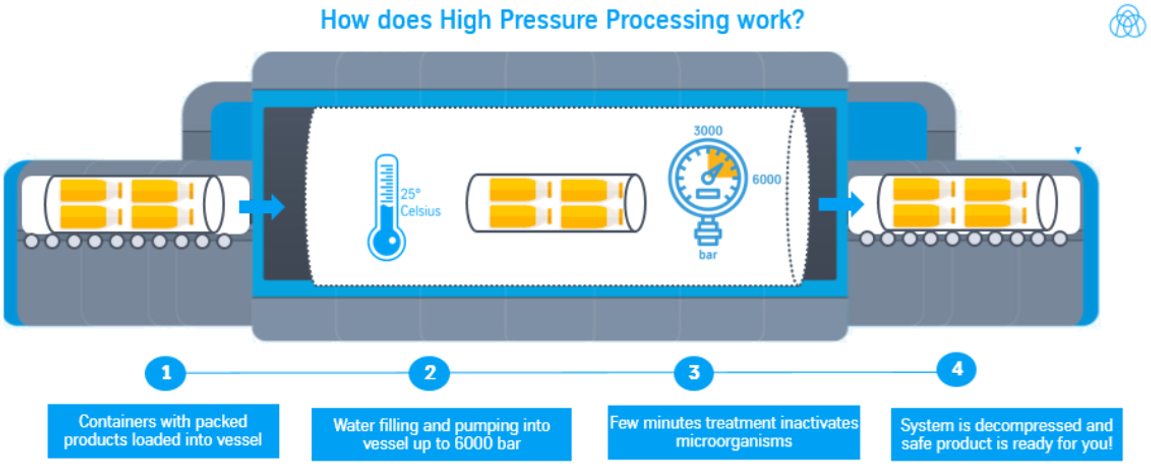
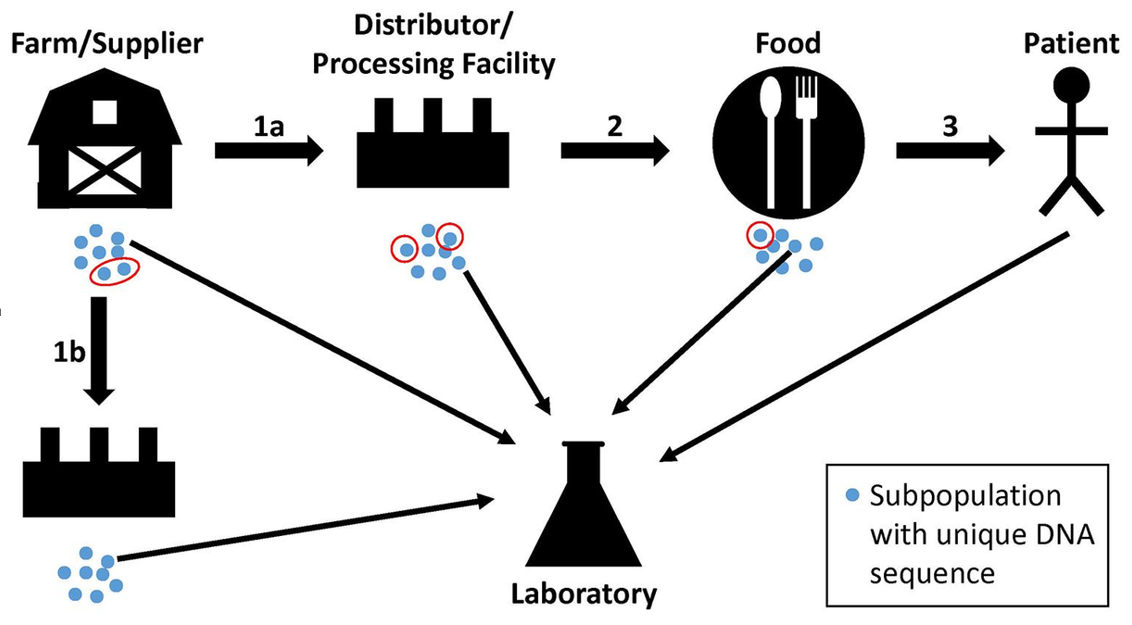 During the 2022 E. coli outbreak in leafy greens,
During the 2022 E. coli outbreak in leafy greens, 


 This allows agencies to prioritize inspections based on actual risk, not just routine schedules.
This allows agencies to prioritize inspections based on actual risk, not just routine schedules.

 General Mills has teamed up with
General Mills has teamed up with 

 This isn’t just about cooking with oil. It’s part of a broader philosophical divide. As institutional trust declines, many are turning to tradition and nature for guidance—assuming, sometimes wrongly, that these values offer more than modern science.
This isn’t just about cooking with oil. It’s part of a broader philosophical divide. As institutional trust declines, many are turning to tradition and nature for guidance—assuming, sometimes wrongly, that these values offer more than modern science.


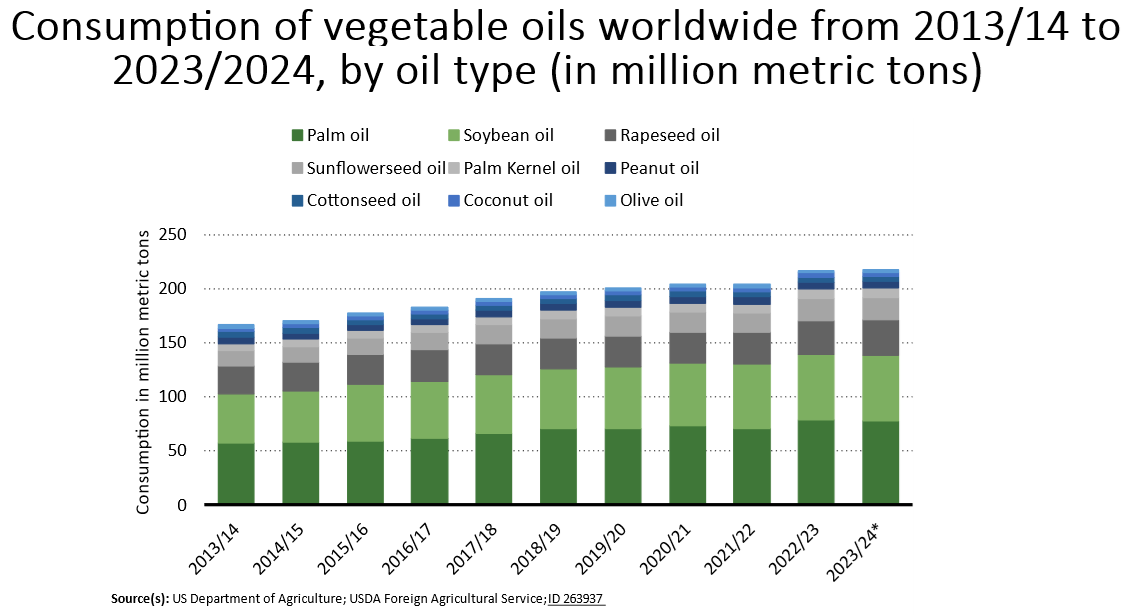
 RFK is right: so many Americans are unhealthy.
RFK is right: so many Americans are unhealthy.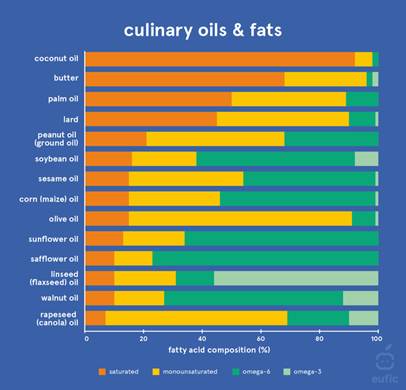
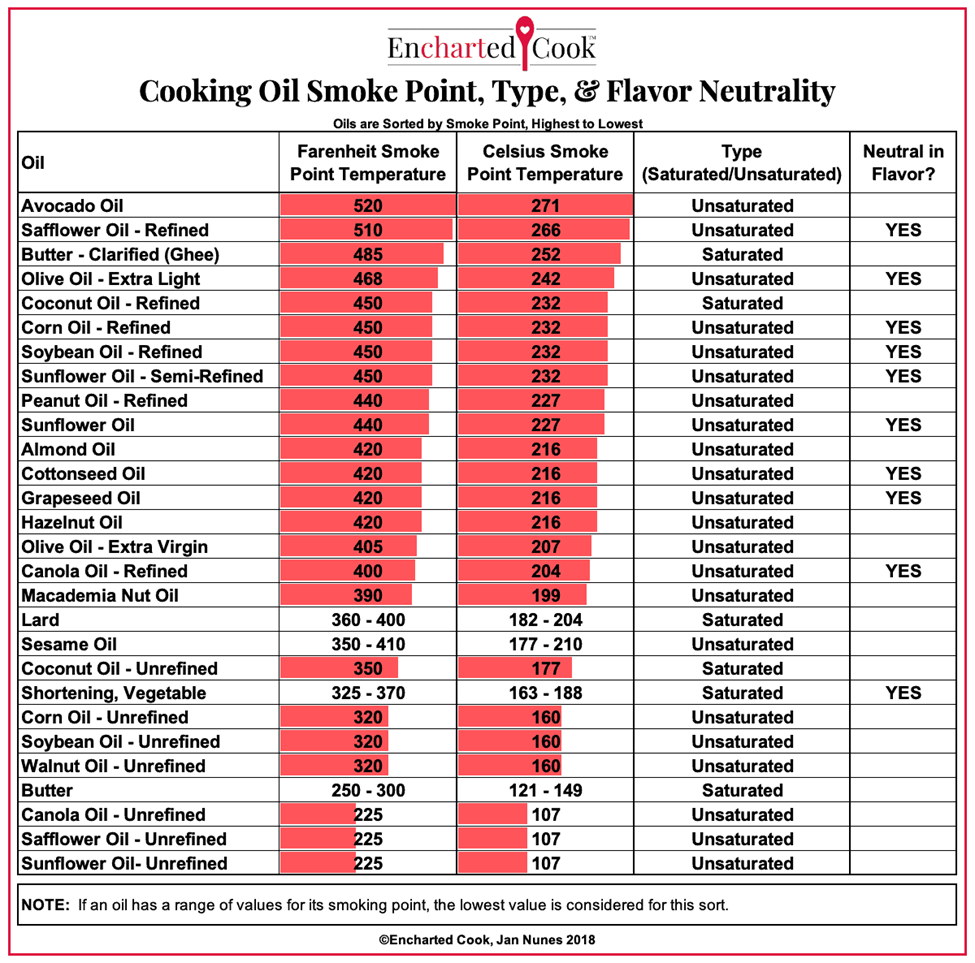










 The Thin Mint headlines may be new, but glyphosate conversations are years old.
The Thin Mint headlines may be new, but glyphosate conversations are years old. Both the
Both the  It’s also important to rinse all
It’s also important to rinse all 

 Brands like
Brands like 

 It doesn’t just kill weeds; it kills anything green, including farm crops such as corn, soybeans, cotton, canola, sugar beets, and alfalfa. These crops have all been genetically modified so that the farmer can spray glyphosate after the crop emerges from the ground and kill the weeds, but not the crop.
It doesn’t just kill weeds; it kills anything green, including farm crops such as corn, soybeans, cotton, canola, sugar beets, and alfalfa. These crops have all been genetically modified so that the farmer can spray glyphosate after the crop emerges from the ground and kill the weeds, but not the crop.

 While there were different views on its effect on soil health, all agreed that it is the least toxic of the herbicides on the market.
While there were different views on its effect on soil health, all agreed that it is the least toxic of the herbicides on the market.
 One farmer invented
One farmer invented 




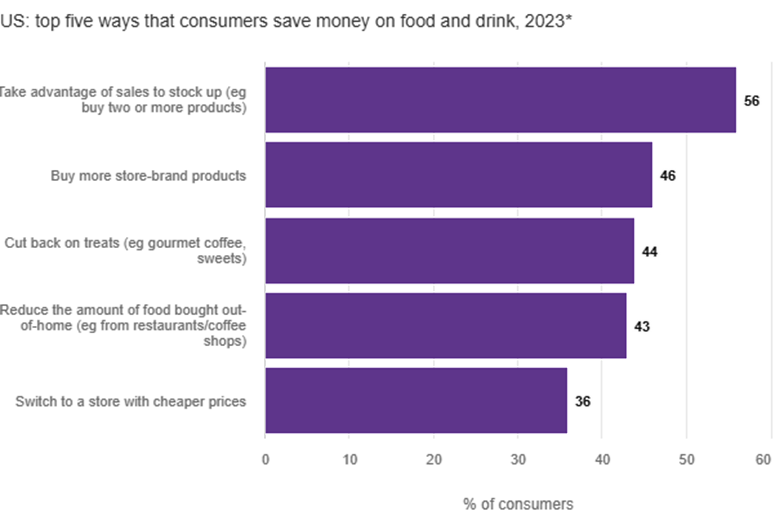
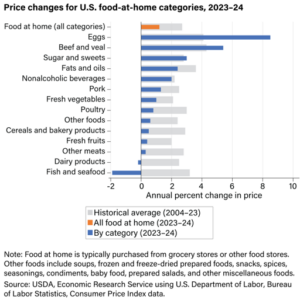 Mostly I look for sales. If it’s a good deal, that’s what we eat.
Mostly I look for sales. If it’s a good deal, that’s what we eat.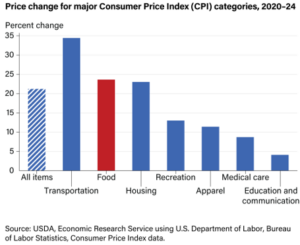 What do you think? Of course they are going to keep going up. Nothing I can do about that.
What do you think? Of course they are going to keep going up. Nothing I can do about that. 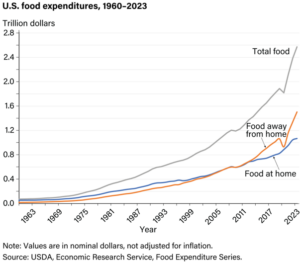 We’ll go out on weekends now and then, but not during the week. And we try to leave the kids home when we do. That saves us a lot of money.
We’ll go out on weekends now and then, but not during the week. And we try to leave the kids home when we do. That saves us a lot of money. 

 In 2023, over
In 2023, over 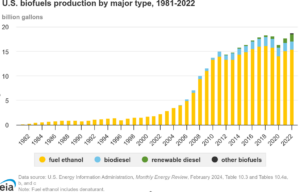

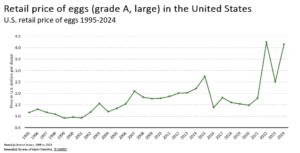
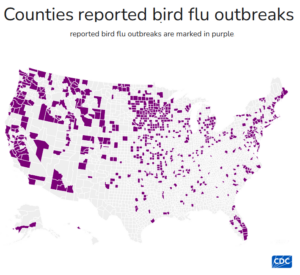
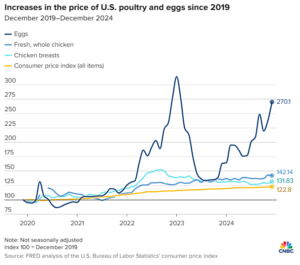
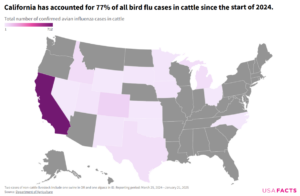
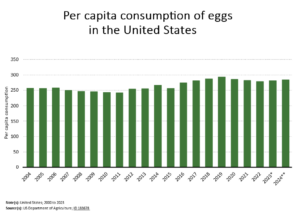
 A local supermarket worker described the retail situation in simple terms: “Eggs come in on Friday’s truck. By Monday, they are pretty much gone.”
A local supermarket worker described the retail situation in simple terms: “Eggs come in on Friday’s truck. By Monday, they are pretty much gone.”

 The FDA’s decision to act on Red Dye No. 3 after decades of inaction may signal a shift towards more proactive regulation of food additives.
The FDA’s decision to act on Red Dye No. 3 after decades of inaction may signal a shift towards more proactive regulation of food additives. There are many substitutes for Red Dye No. 3, such as beet juice, purple sweet potato extract, red cabbage extract, carmine, and pomegranate juice. These natural substitutes align with growing consumer preferences for clean-label ingredients. After all, many of us would rather consume pomegranate juice in Jell-o than red dye.
There are many substitutes for Red Dye No. 3, such as beet juice, purple sweet potato extract, red cabbage extract, carmine, and pomegranate juice. These natural substitutes align with growing consumer preferences for clean-label ingredients. After all, many of us would rather consume pomegranate juice in Jell-o than red dye.
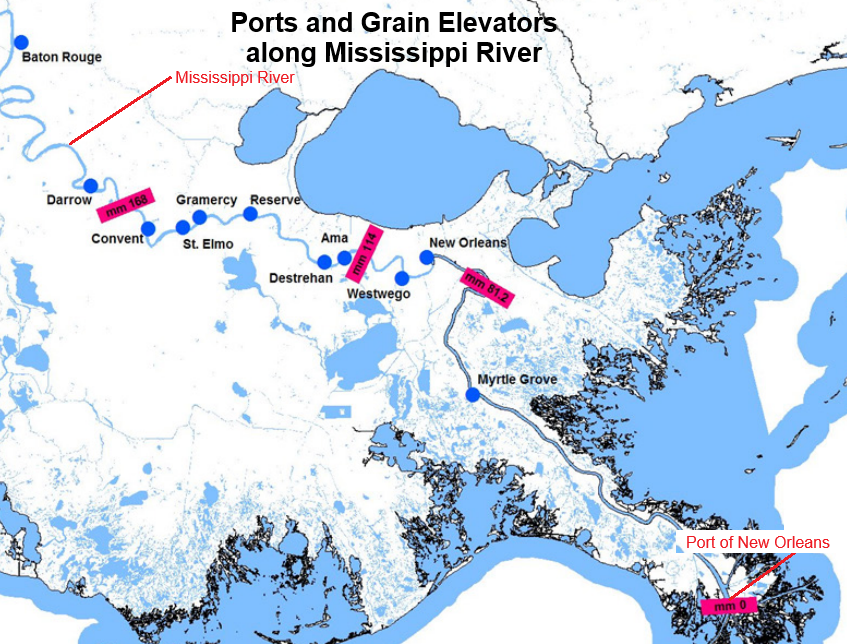
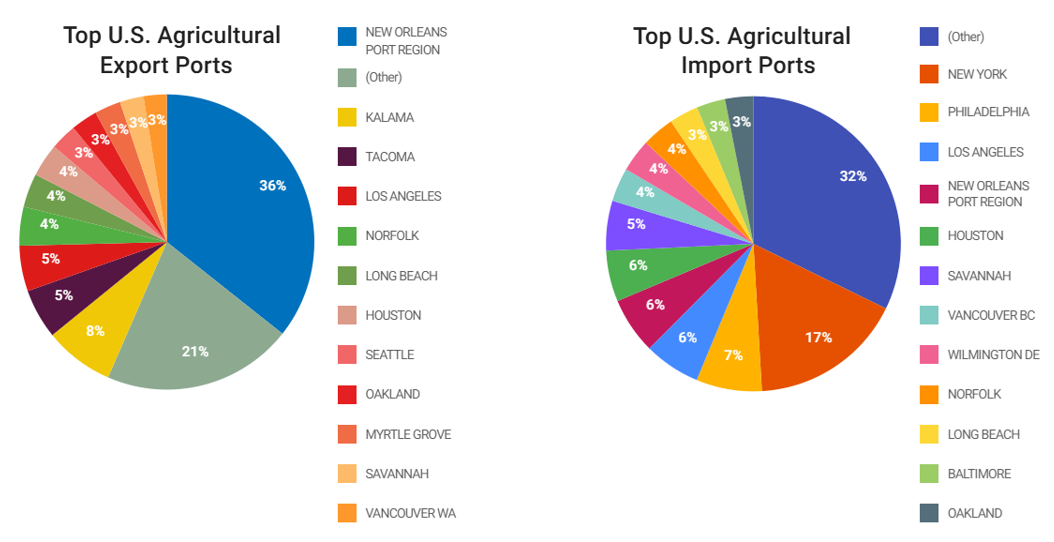
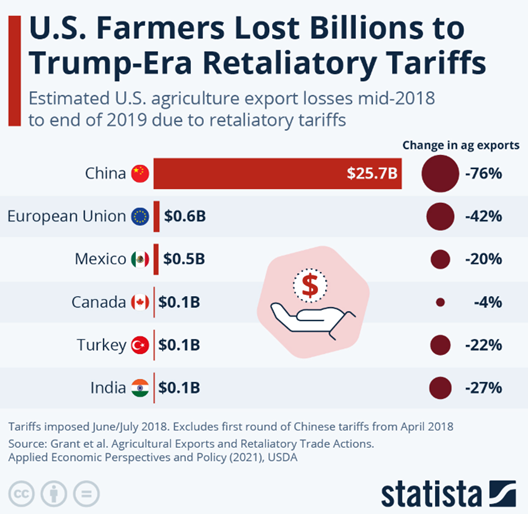
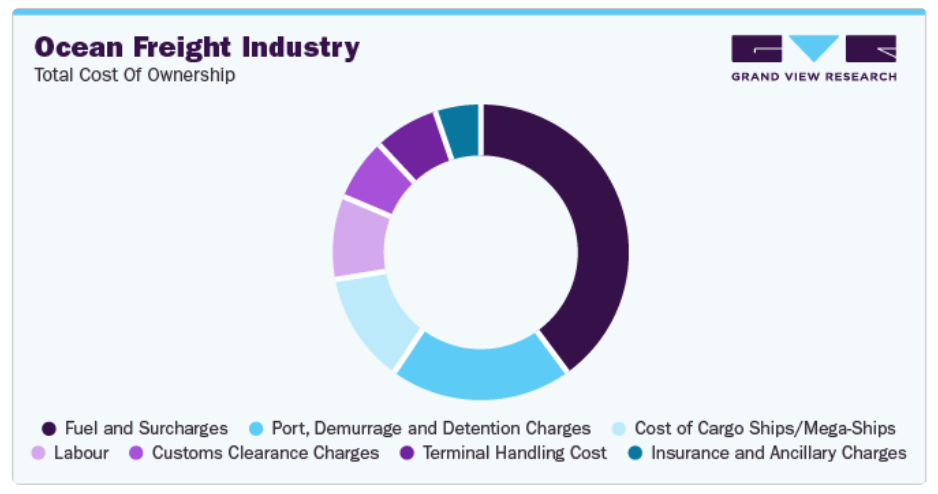
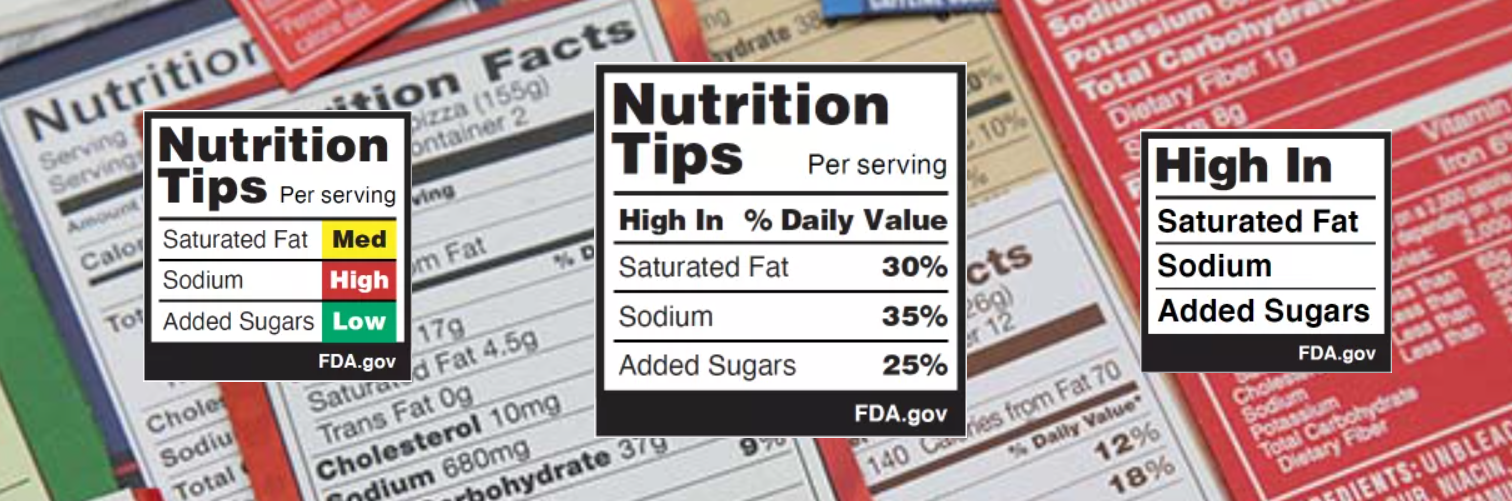
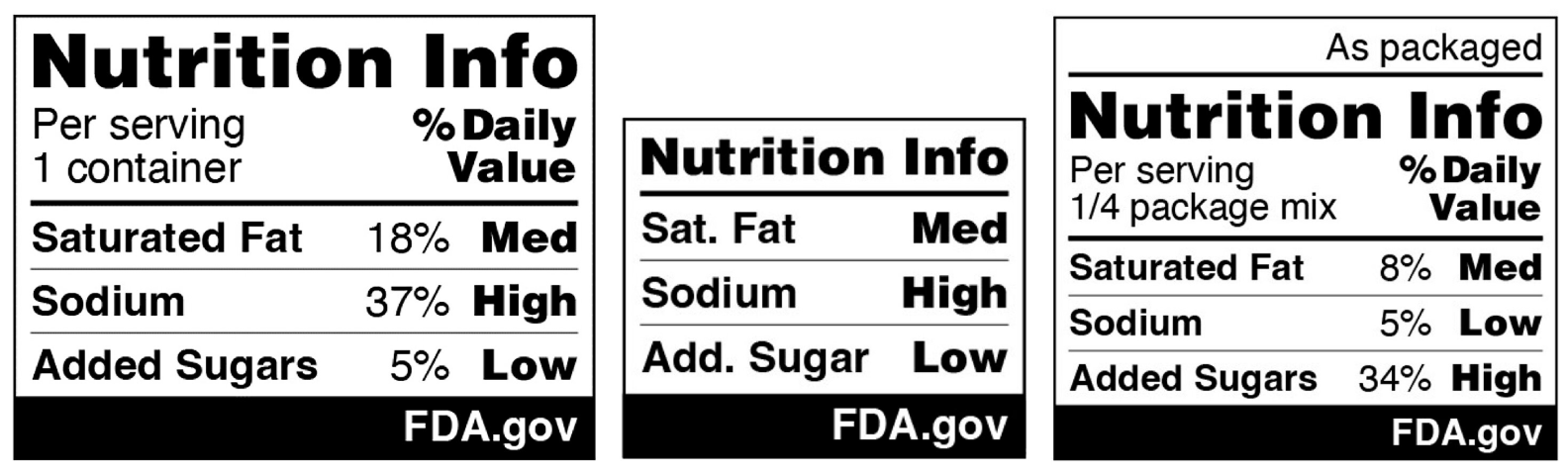
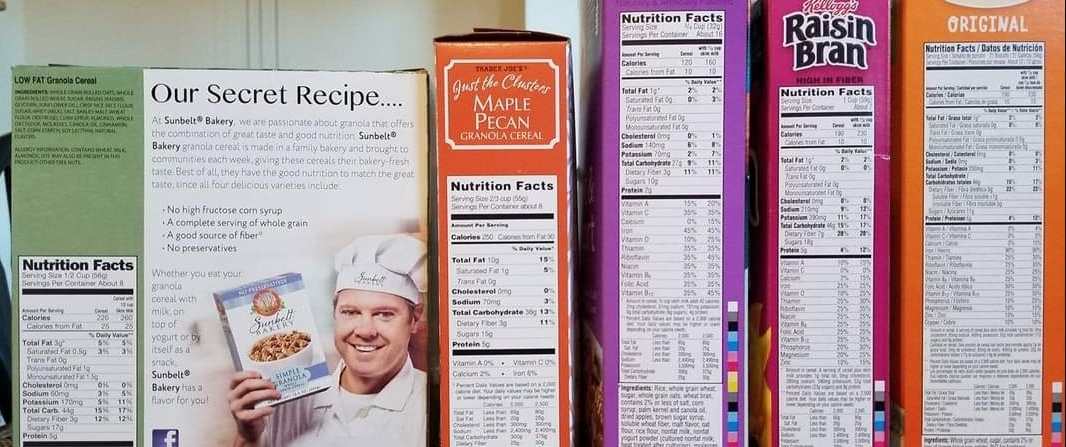

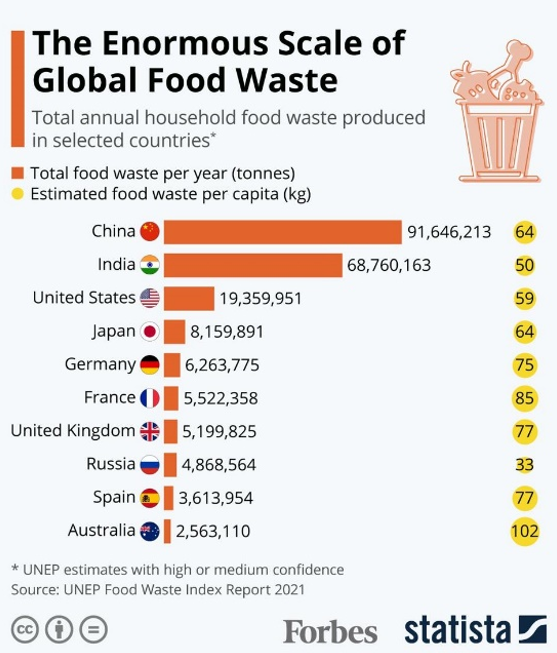 It also illustrates the systemic inefficiencies in food supply chains, from overproduction and spoilage during transport, to the rejection of perfectly good produce due to cosmetic imperfections.
It also illustrates the systemic inefficiencies in food supply chains, from overproduction and spoilage during transport, to the rejection of perfectly good produce due to cosmetic imperfections.

 Peter Attia, MD, who wrote Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity, points to VO2 max as the best predictor of longevity.
Peter Attia, MD, who wrote Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity, points to VO2 max as the best predictor of longevity.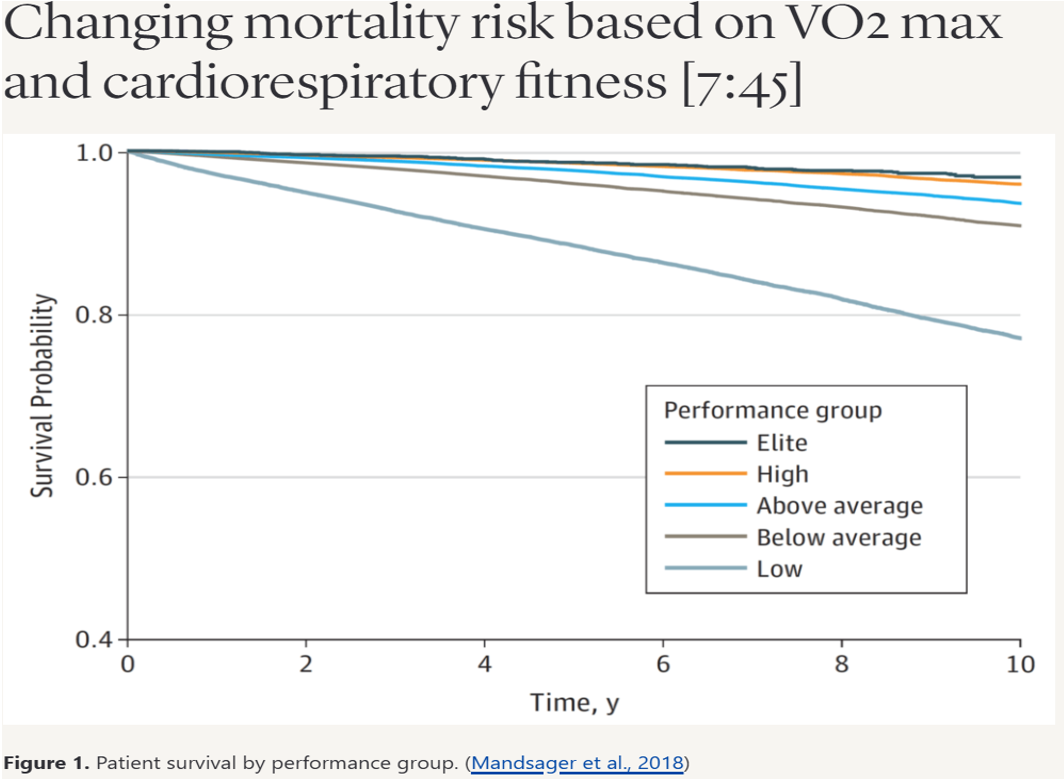
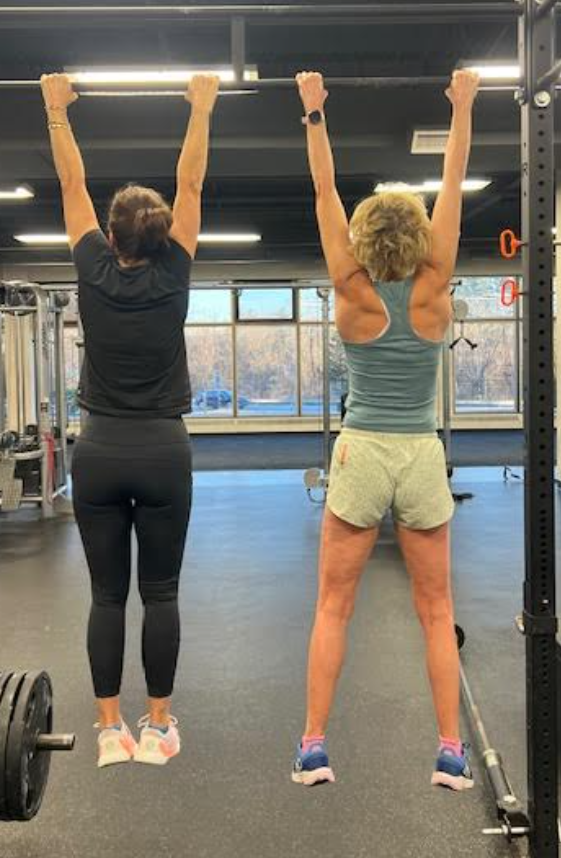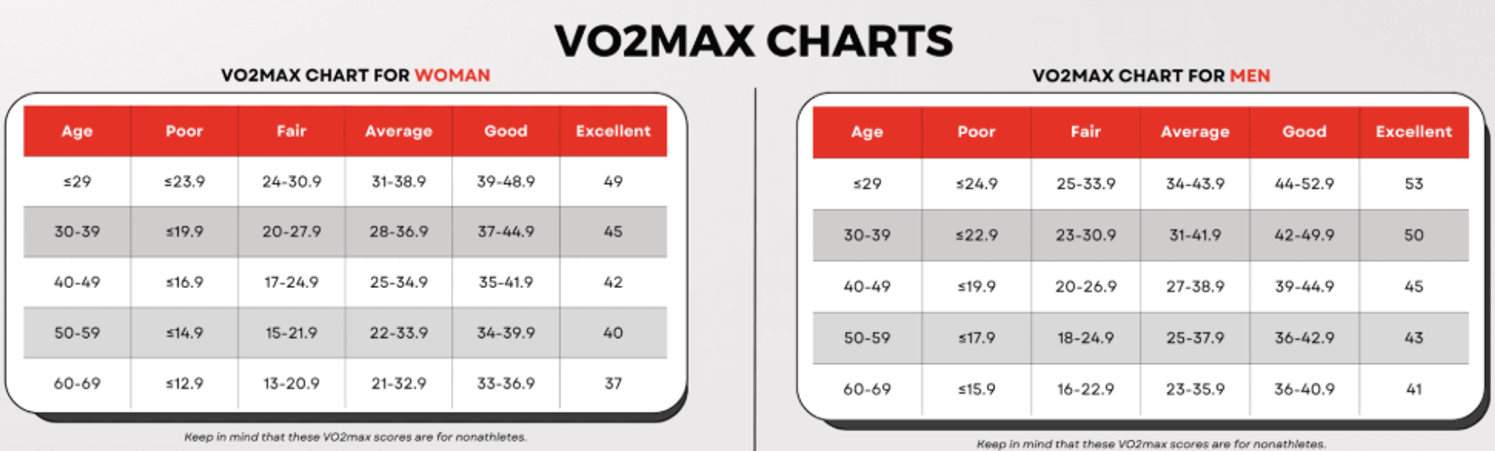
 Hanging from a bar measures your grip strength, which measures your overall muscle ratio – a good indicator of overall fitness.
Hanging from a bar measures your grip strength, which measures your overall muscle ratio – a good indicator of overall fitness.
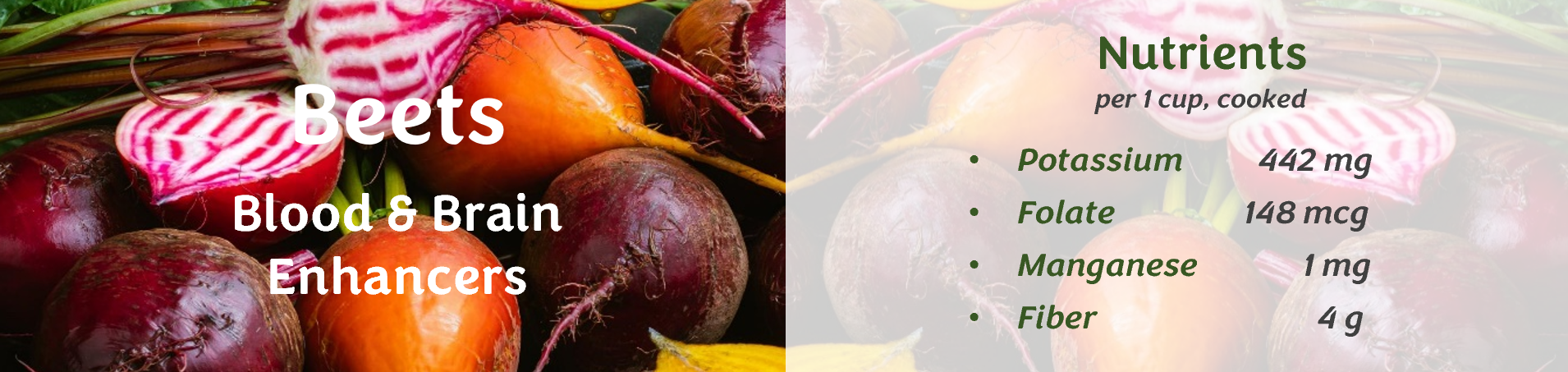
 Spinach:
Spinach: 
 Sustainability is no longer a buzzword but a mandate.
Sustainability is no longer a buzzword but a mandate. 
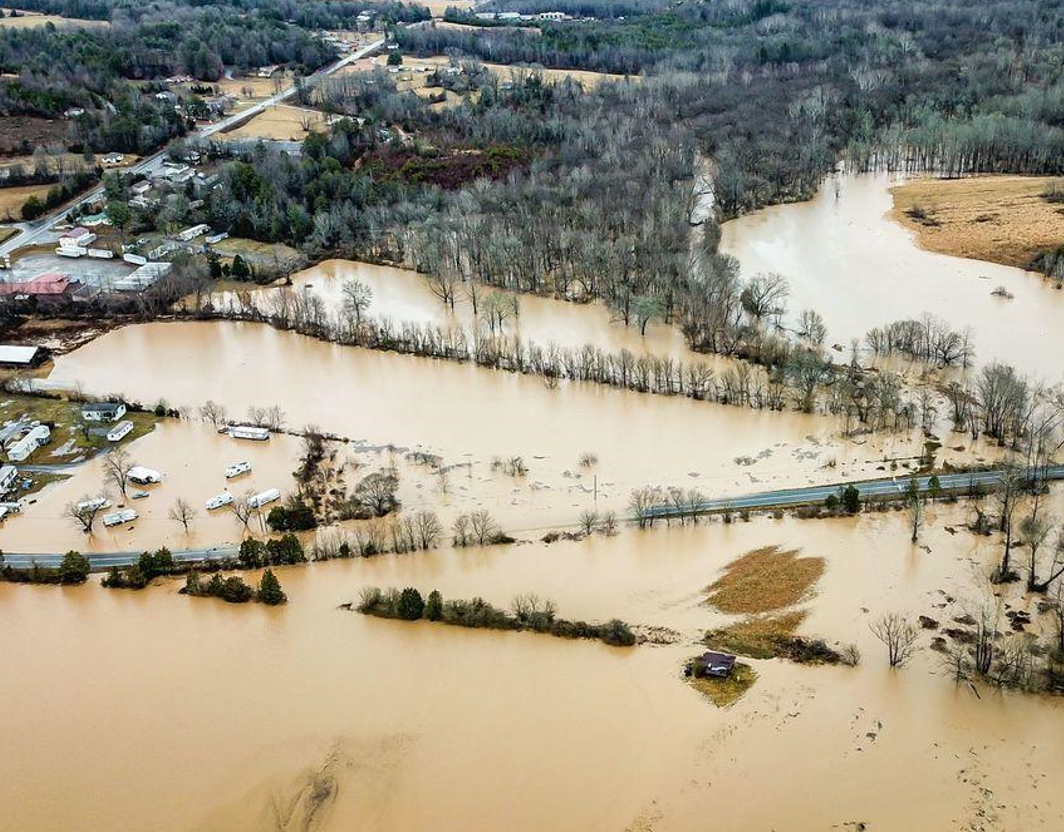





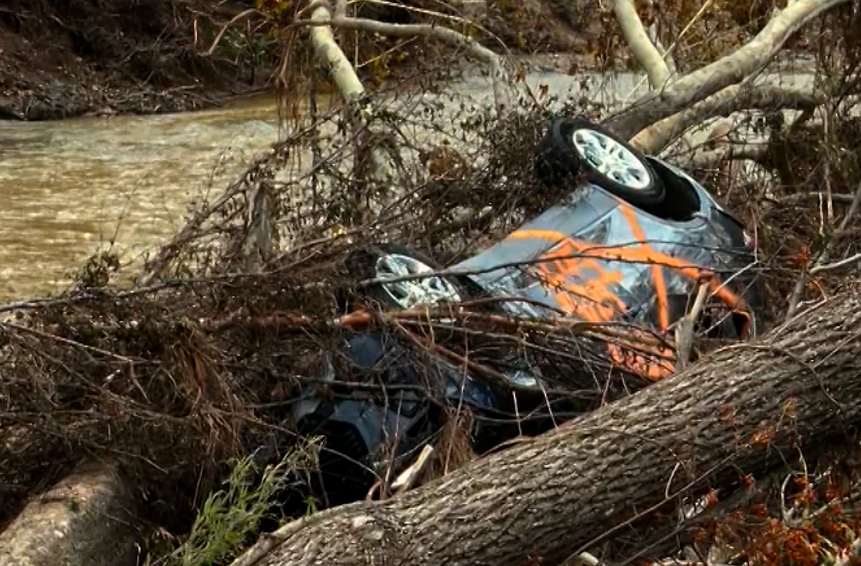
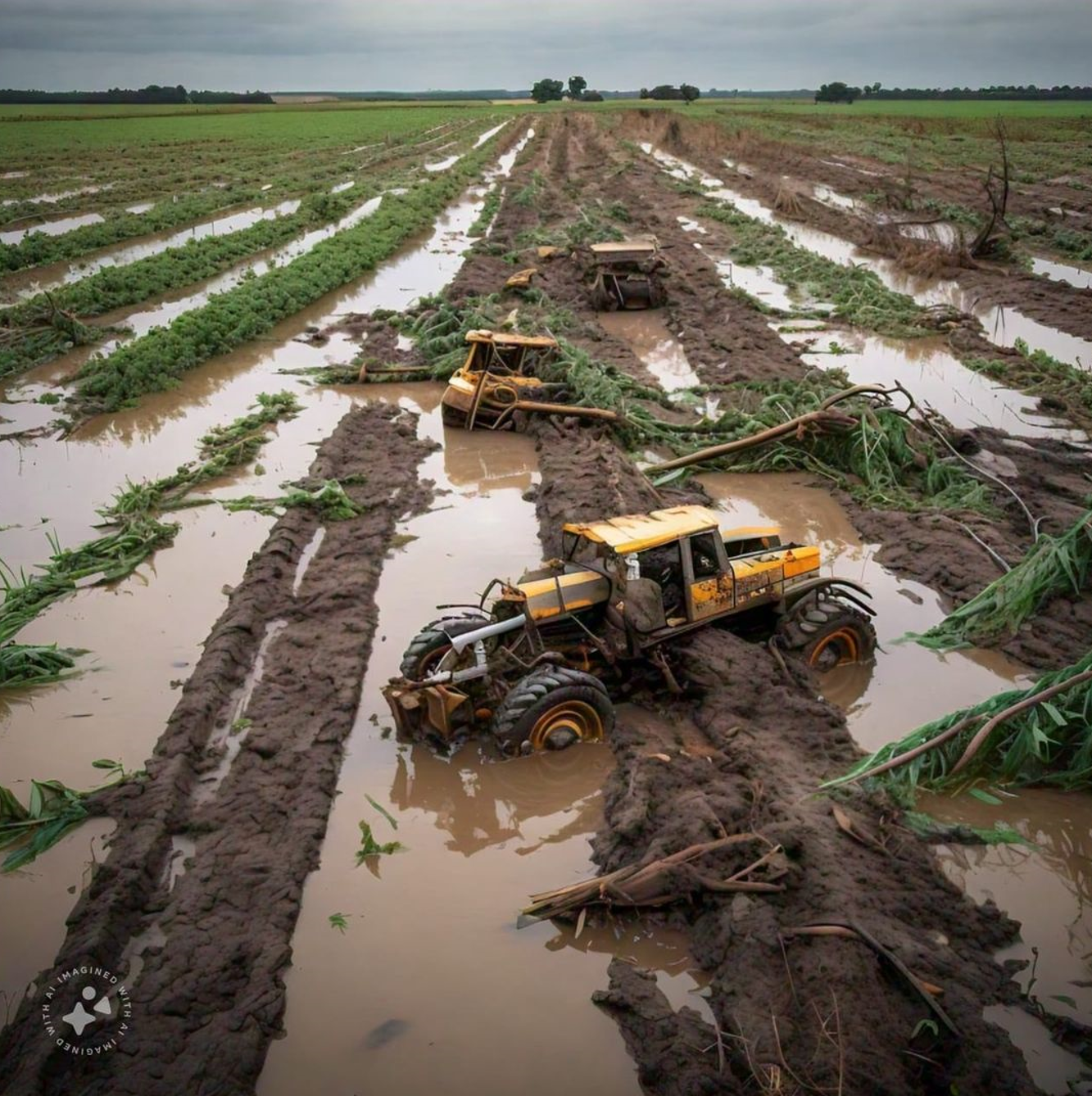
 My part of North Carolina was hit especially hard, with epic flooding and devastation that simply wiped away many of the small towns here and left cities like Asheville reeling from destruction almost beyond description. The photo on the right shows Helene’s impact on my hometown.
My part of North Carolina was hit especially hard, with epic flooding and devastation that simply wiped away many of the small towns here and left cities like Asheville reeling from destruction almost beyond description. The photo on the right shows Helene’s impact on my hometown.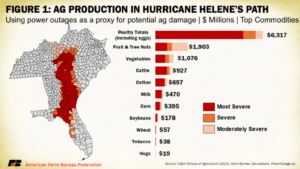















 You wonder: are your children charging too much? So you go back and encourage them to drop their price to $1.00, knowing that at least they should make $25.00 for the day. This will take most of the summer, but an iPhone is still in their future. Life is good.
You wonder: are your children charging too much? So you go back and encourage them to drop their price to $1.00, knowing that at least they should make $25.00 for the day. This will take most of the summer, but an iPhone is still in their future. Life is good.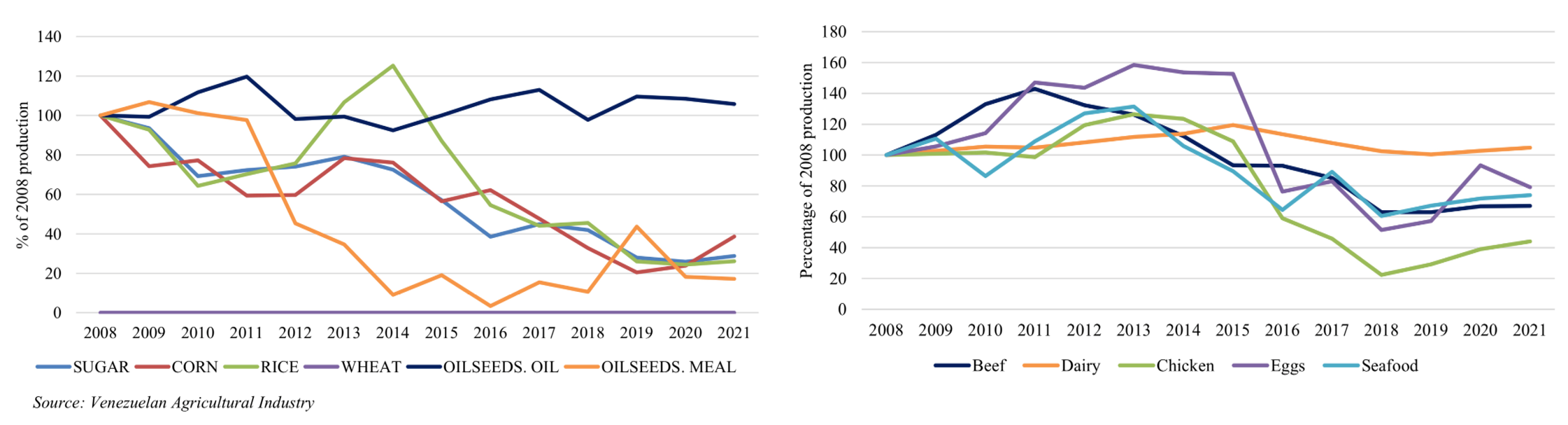
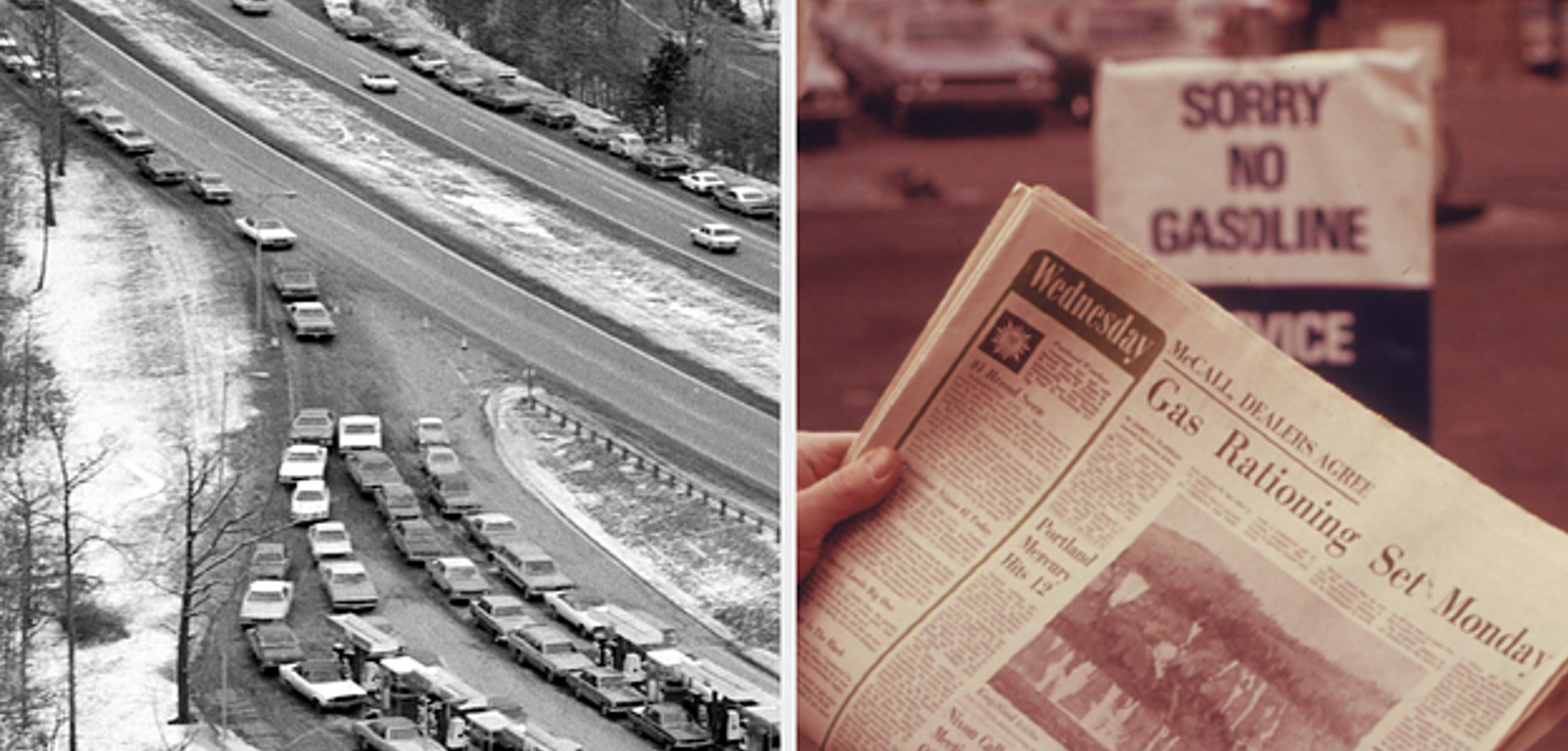









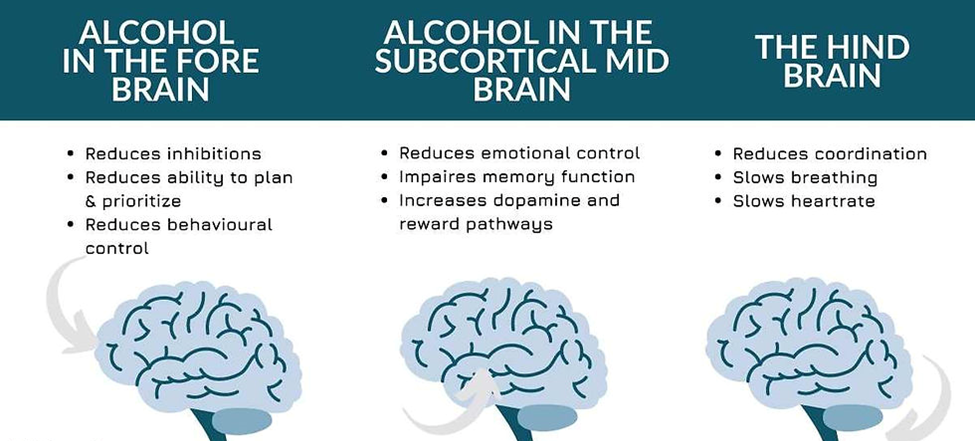
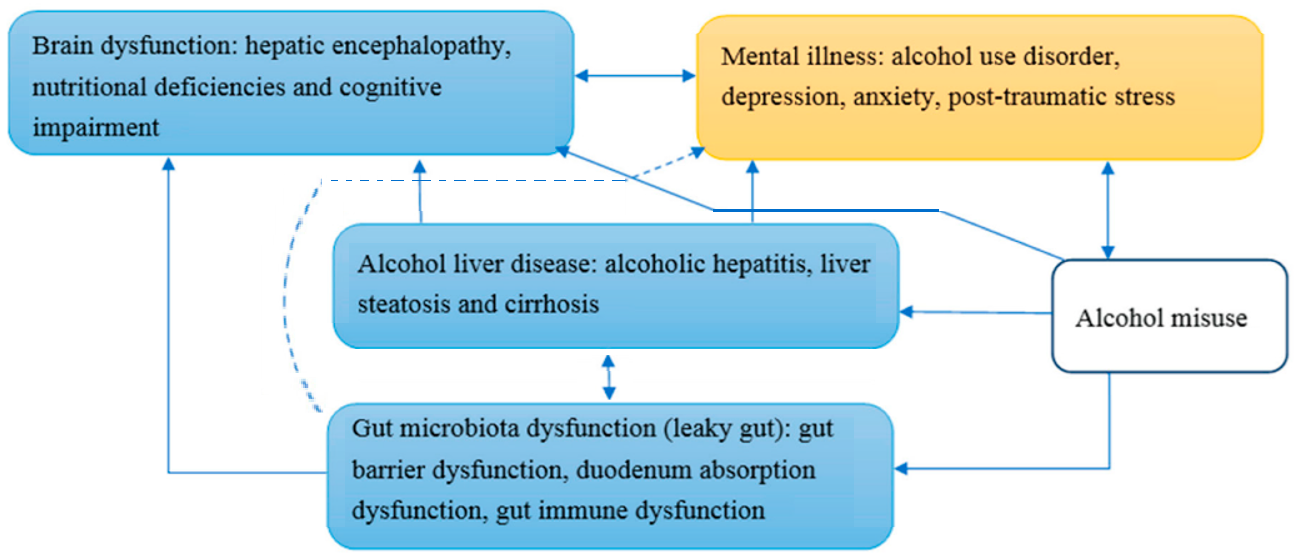
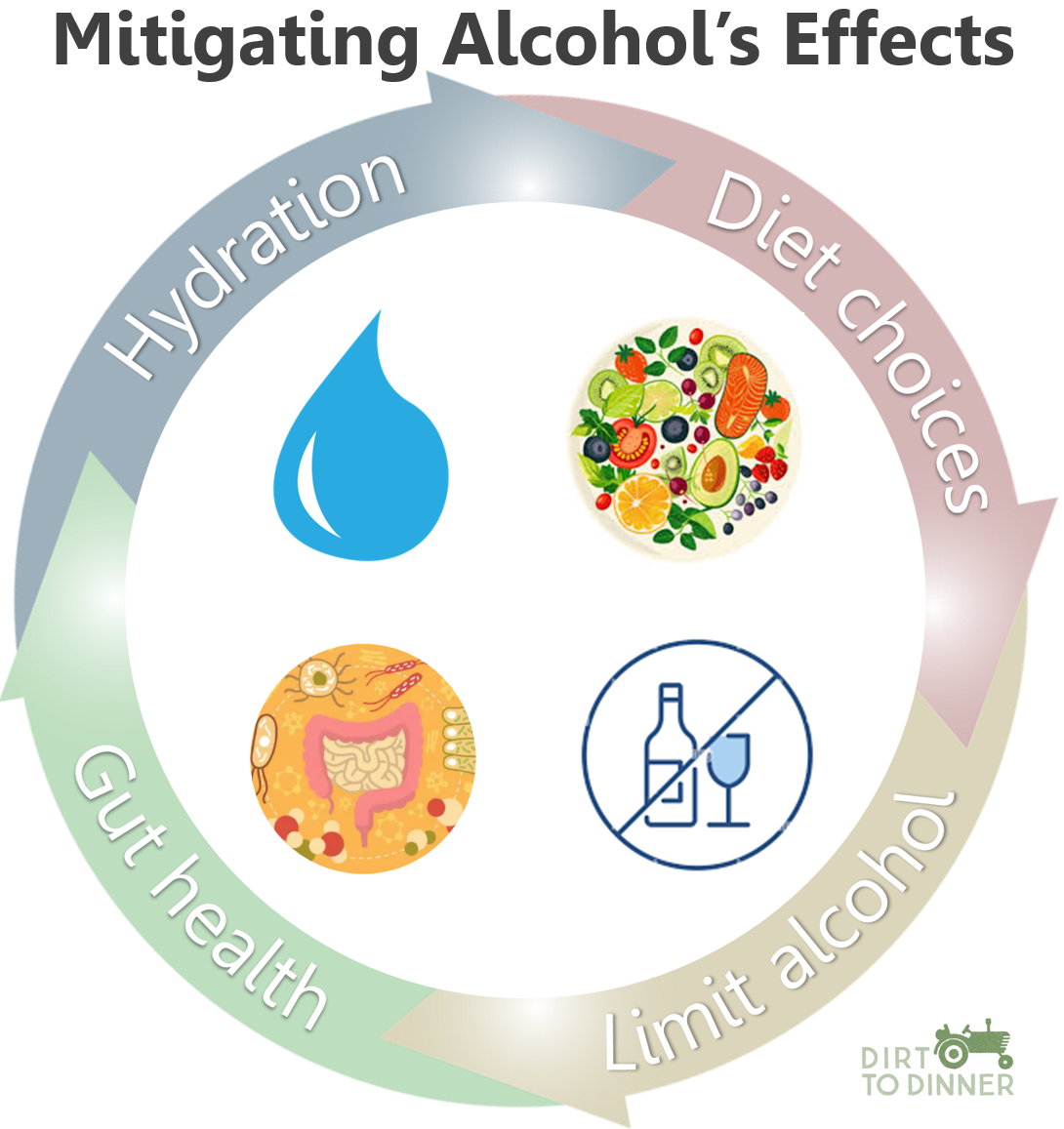









 We’re still without our long-overdue
We’re still without our long-overdue 
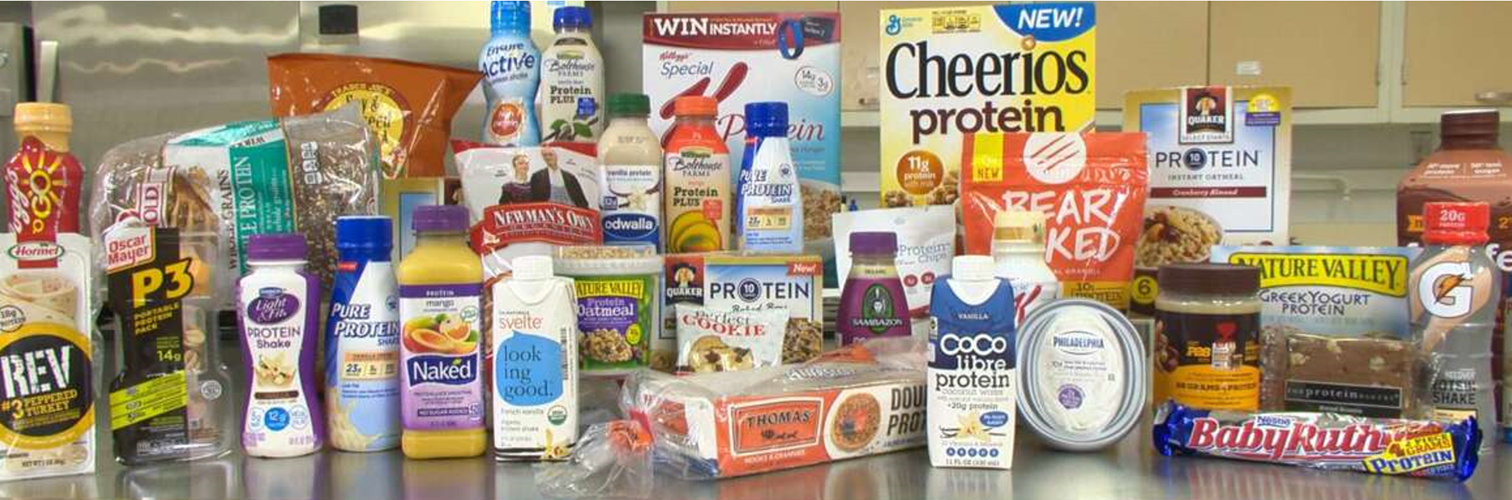
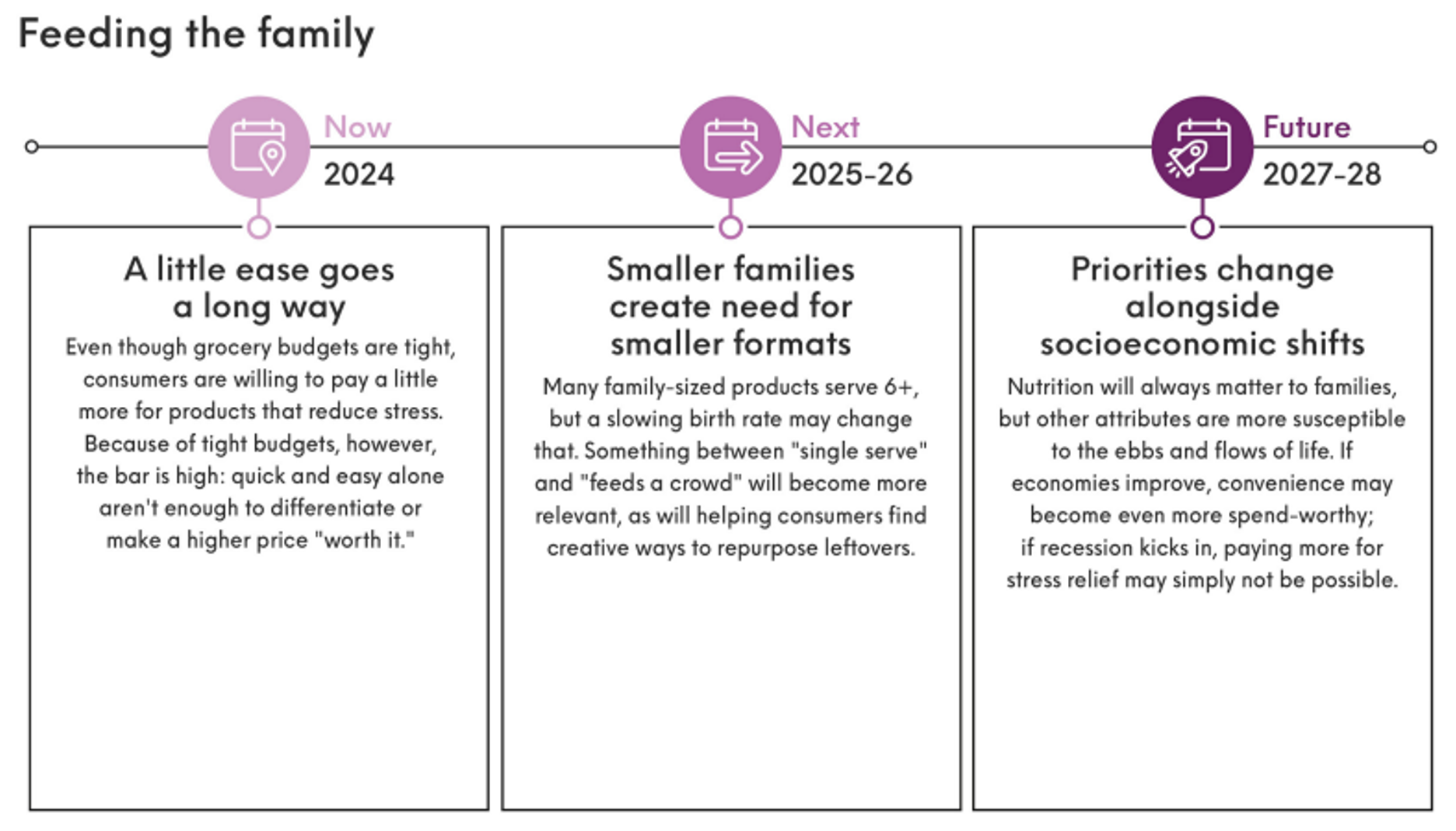

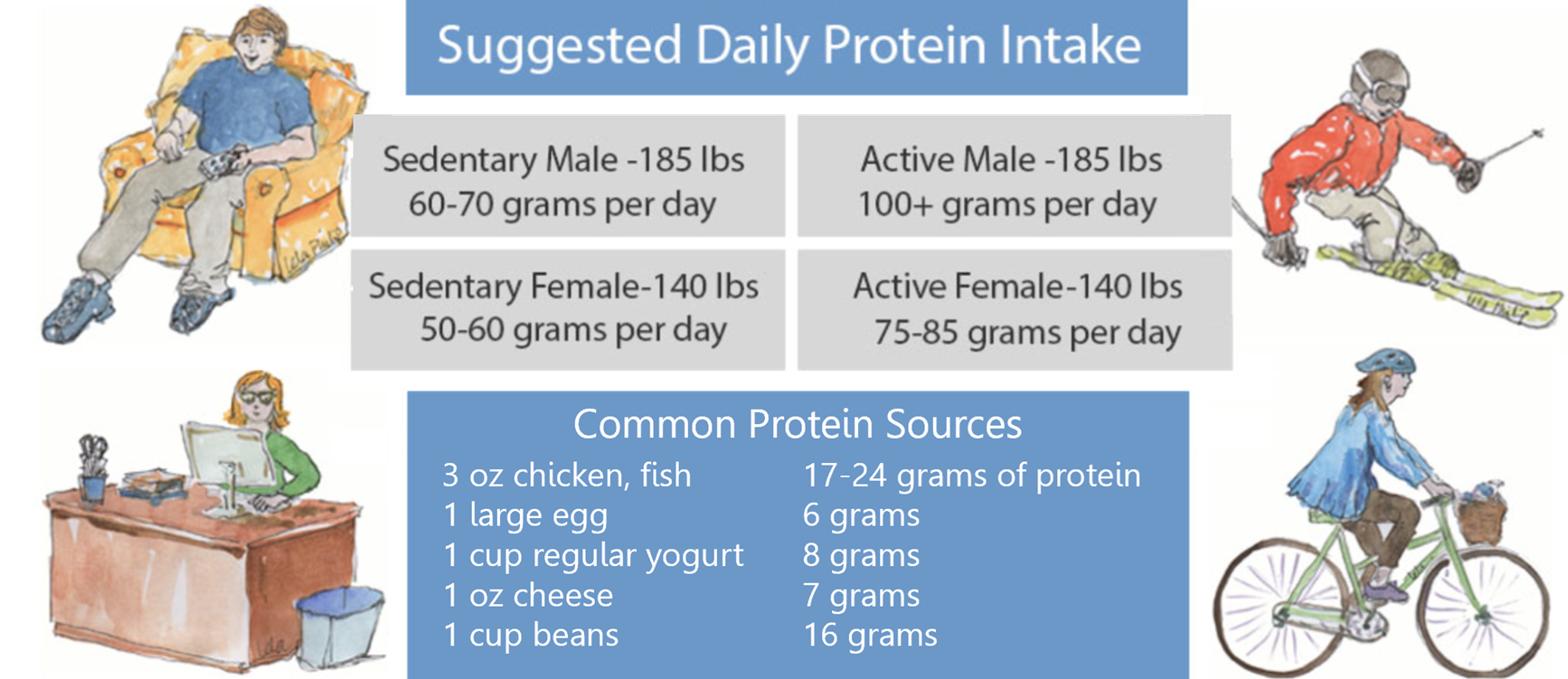
 While protein can help you feel full and satisfied, consuming more protein than your body needs doesn’t magically become muscle…
While protein can help you feel full and satisfied, consuming more protein than your body needs doesn’t magically become muscle…
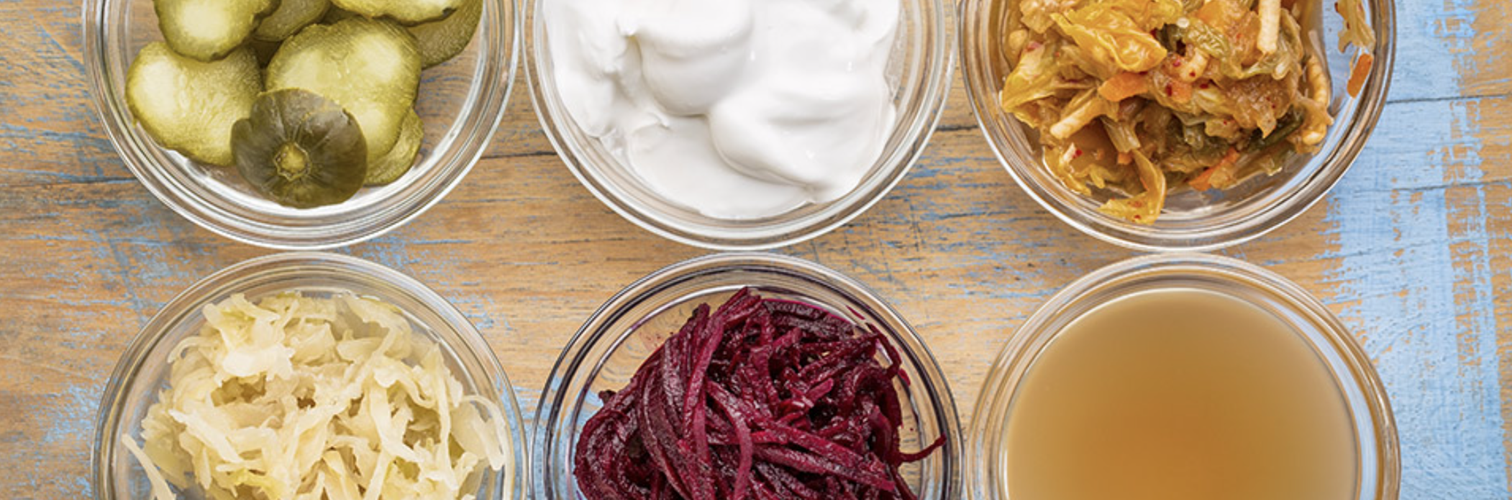




 They’re found in almost every culture and cuisine. Historians
They’re found in almost every culture and cuisine. Historians 
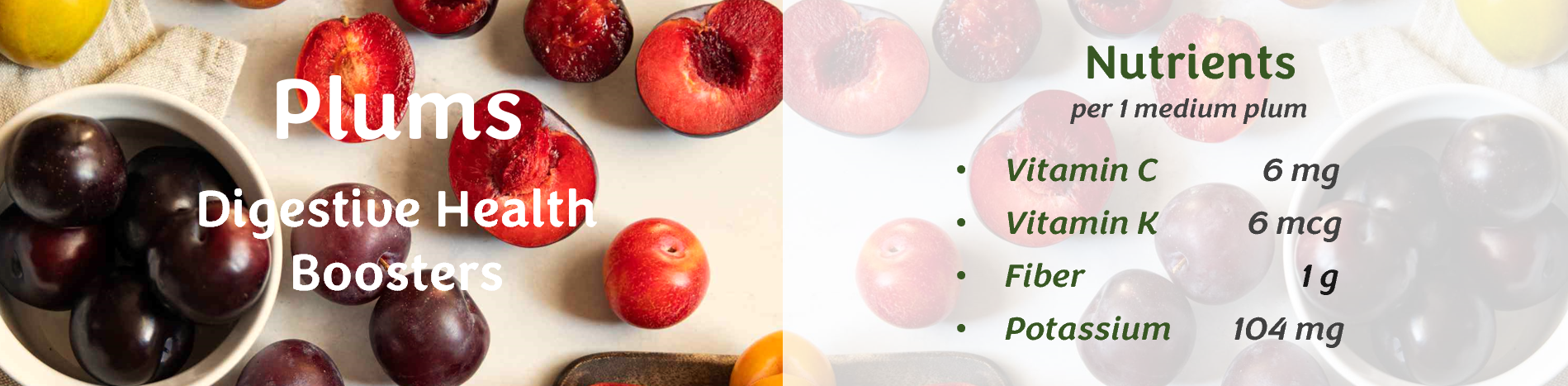
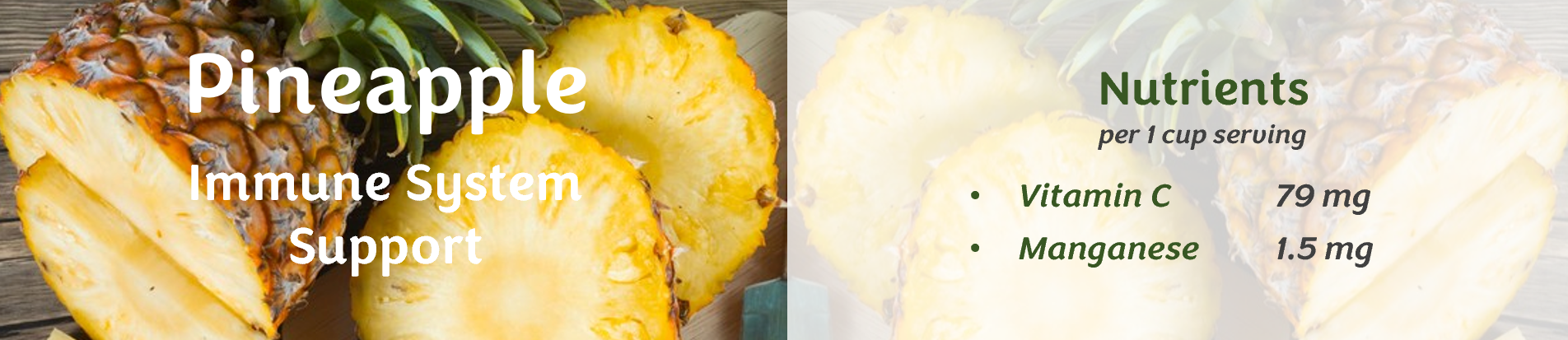
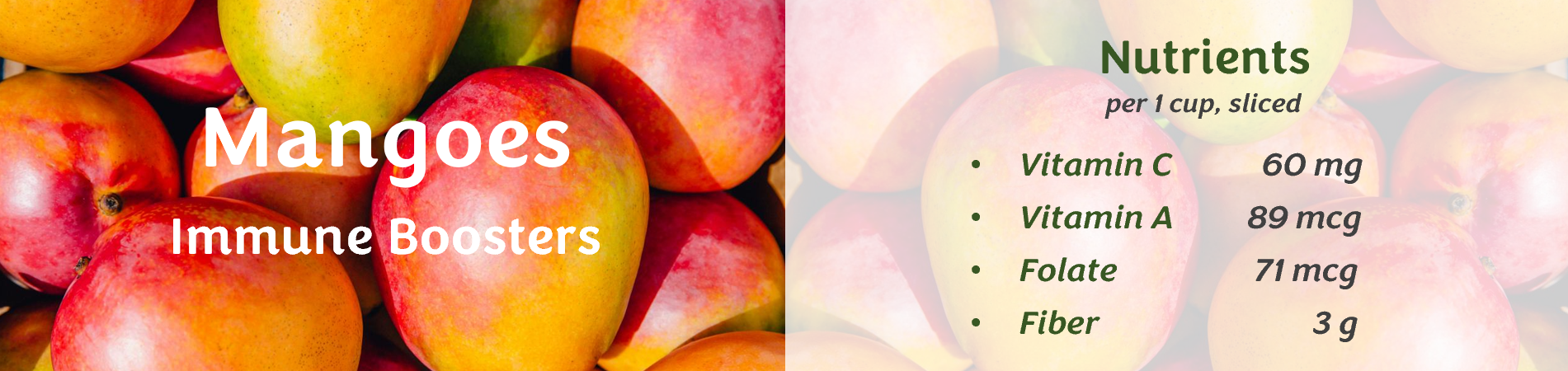
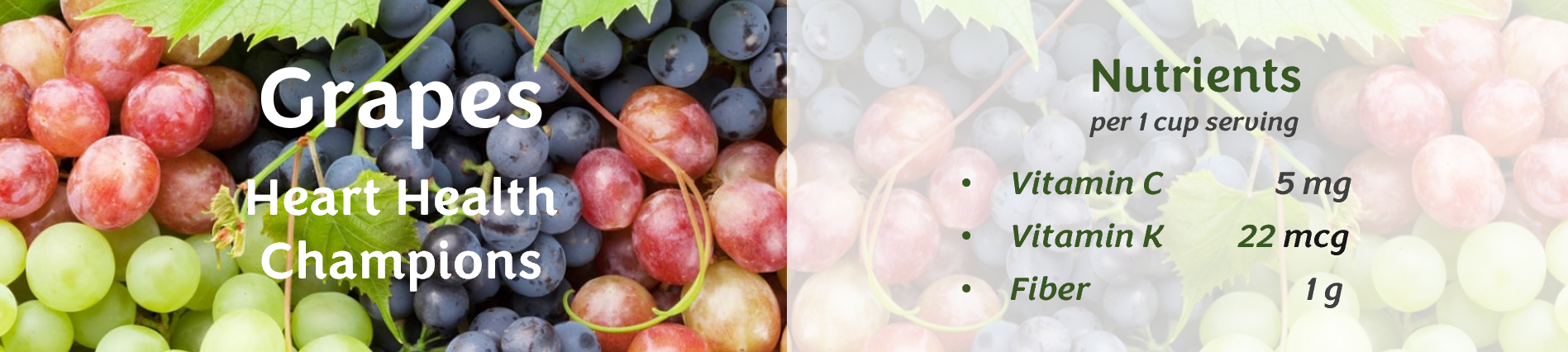
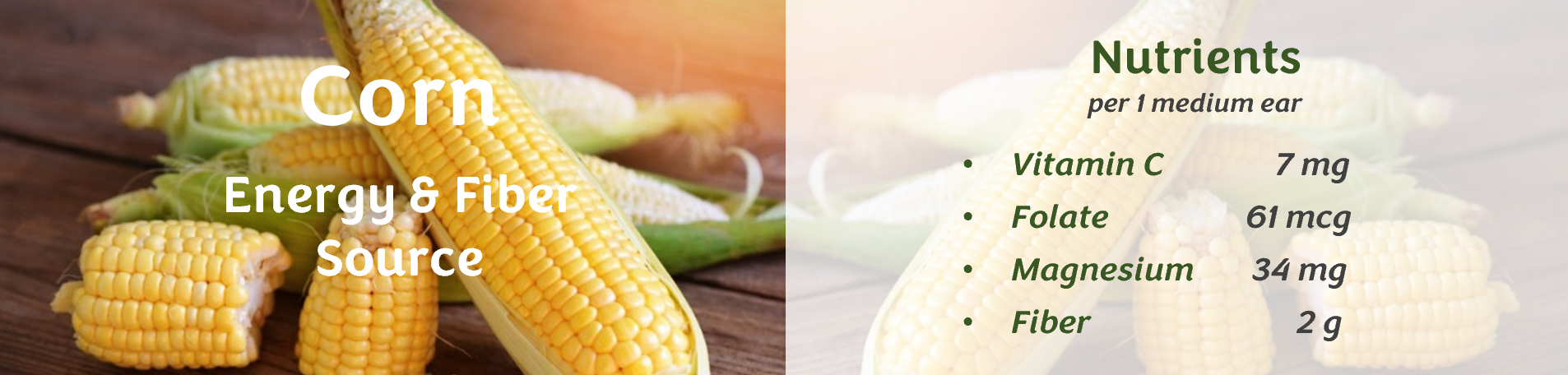





























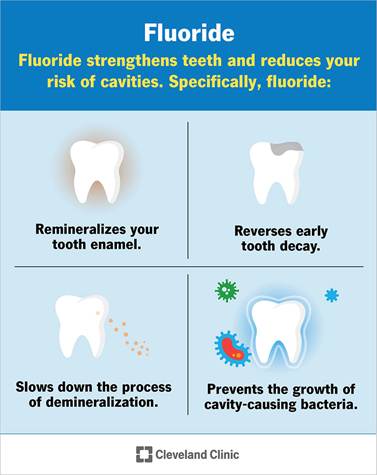
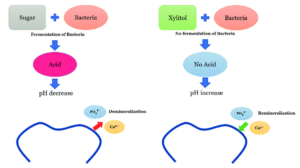 Dental benefits
Dental benefits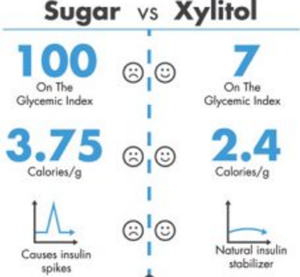 Glycemic control
Glycemic control





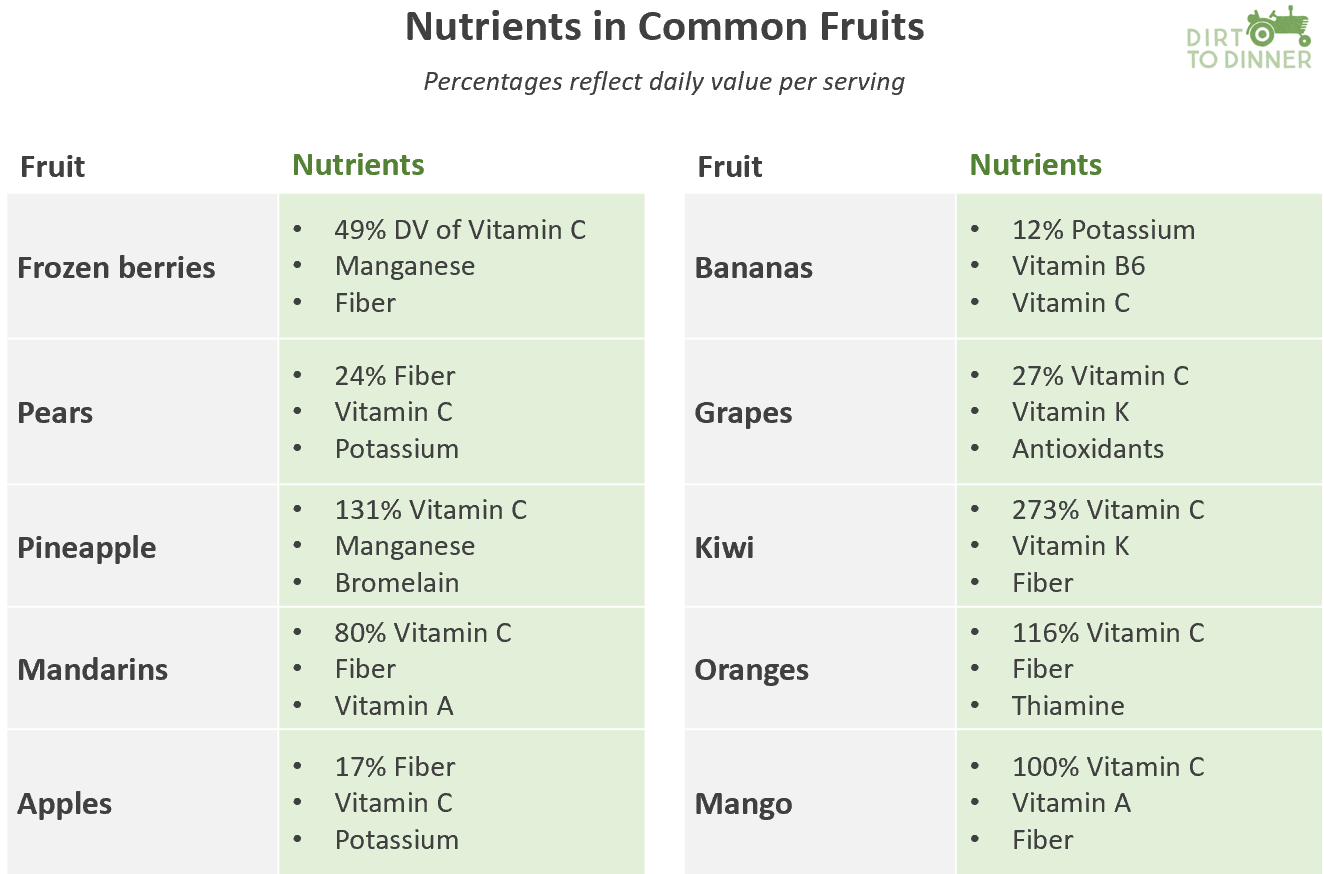
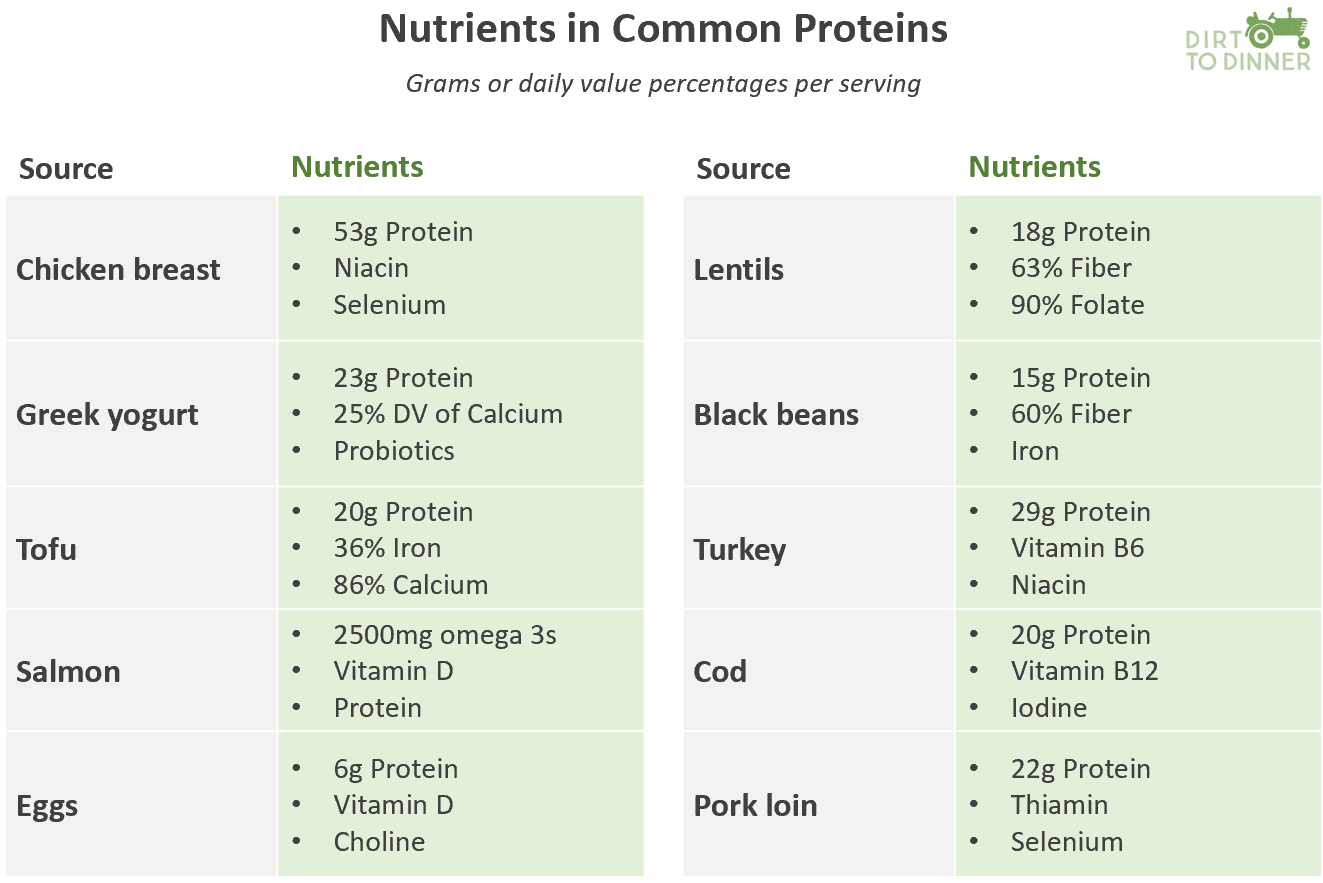

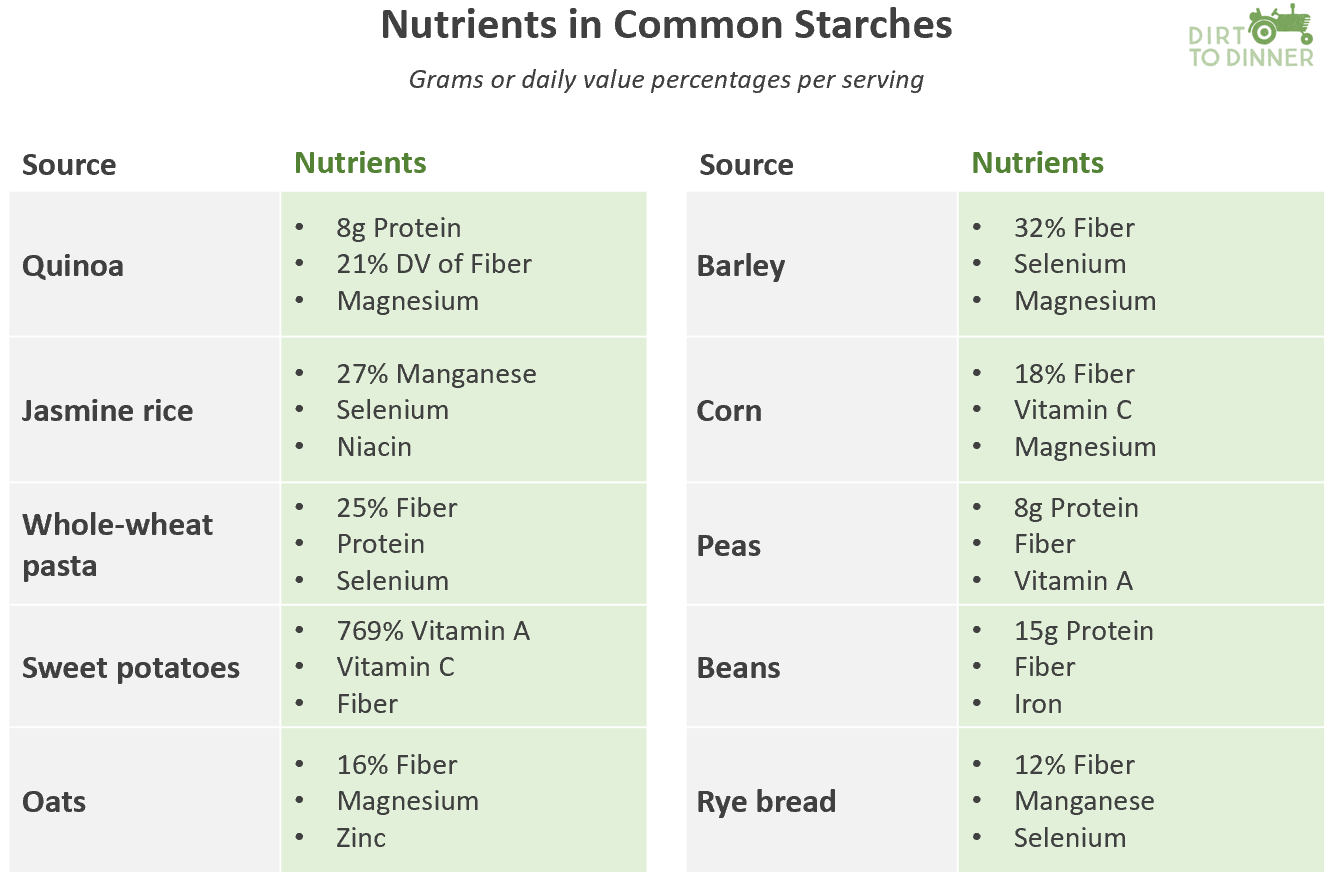






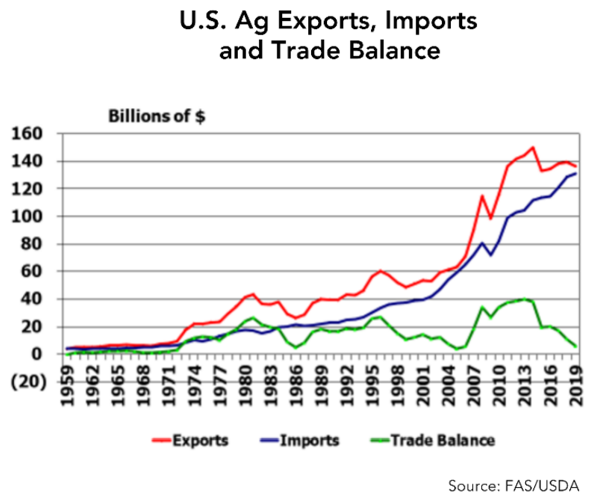
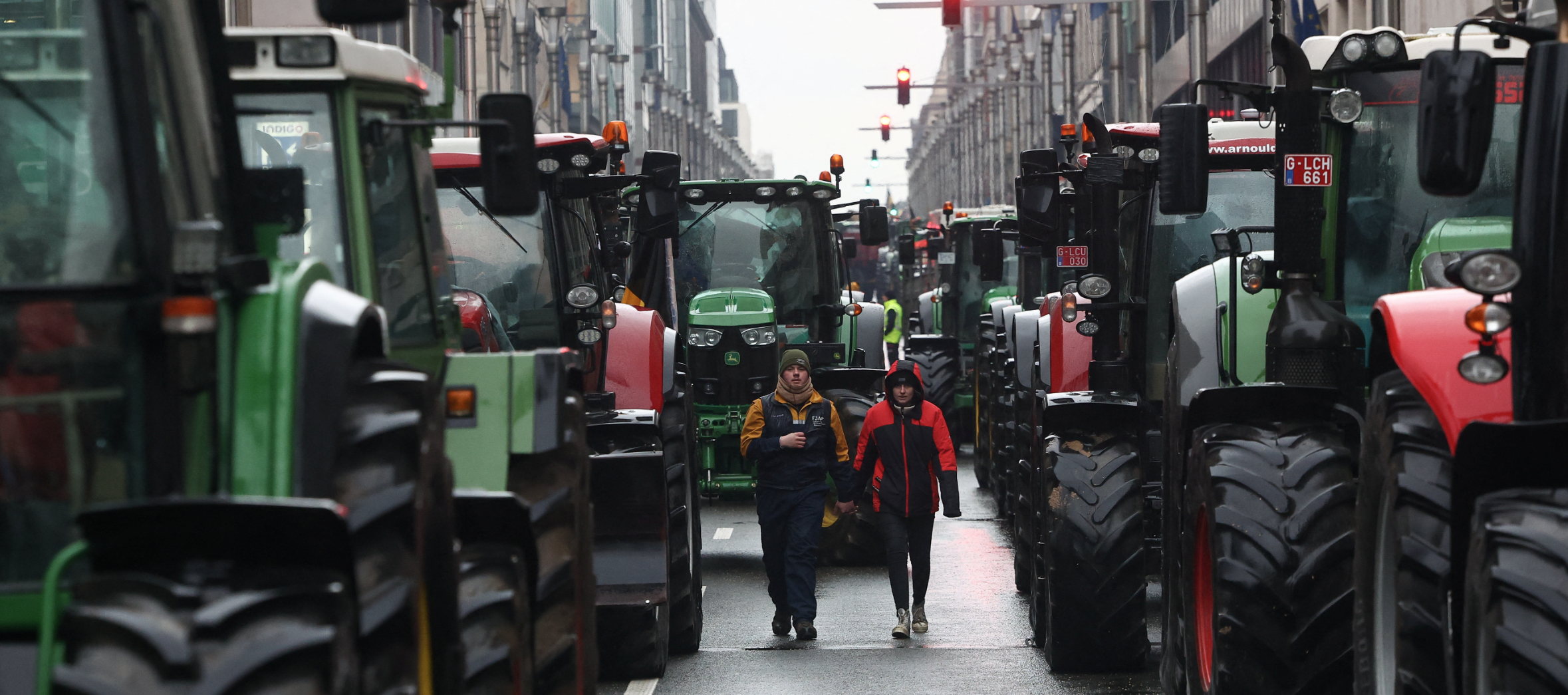
 Moving to vehicles not dependent on fossil fuels is a noble objective. But once again, the reality is that such a transformation in a system as large as the U.S. food system will be an expensive proposition. The more rapid the required conversion, the higher the risk of short-term adverse effects on the producer bottom-line.
Moving to vehicles not dependent on fossil fuels is a noble objective. But once again, the reality is that such a transformation in a system as large as the U.S. food system will be an expensive proposition. The more rapid the required conversion, the higher the risk of short-term adverse effects on the producer bottom-line.
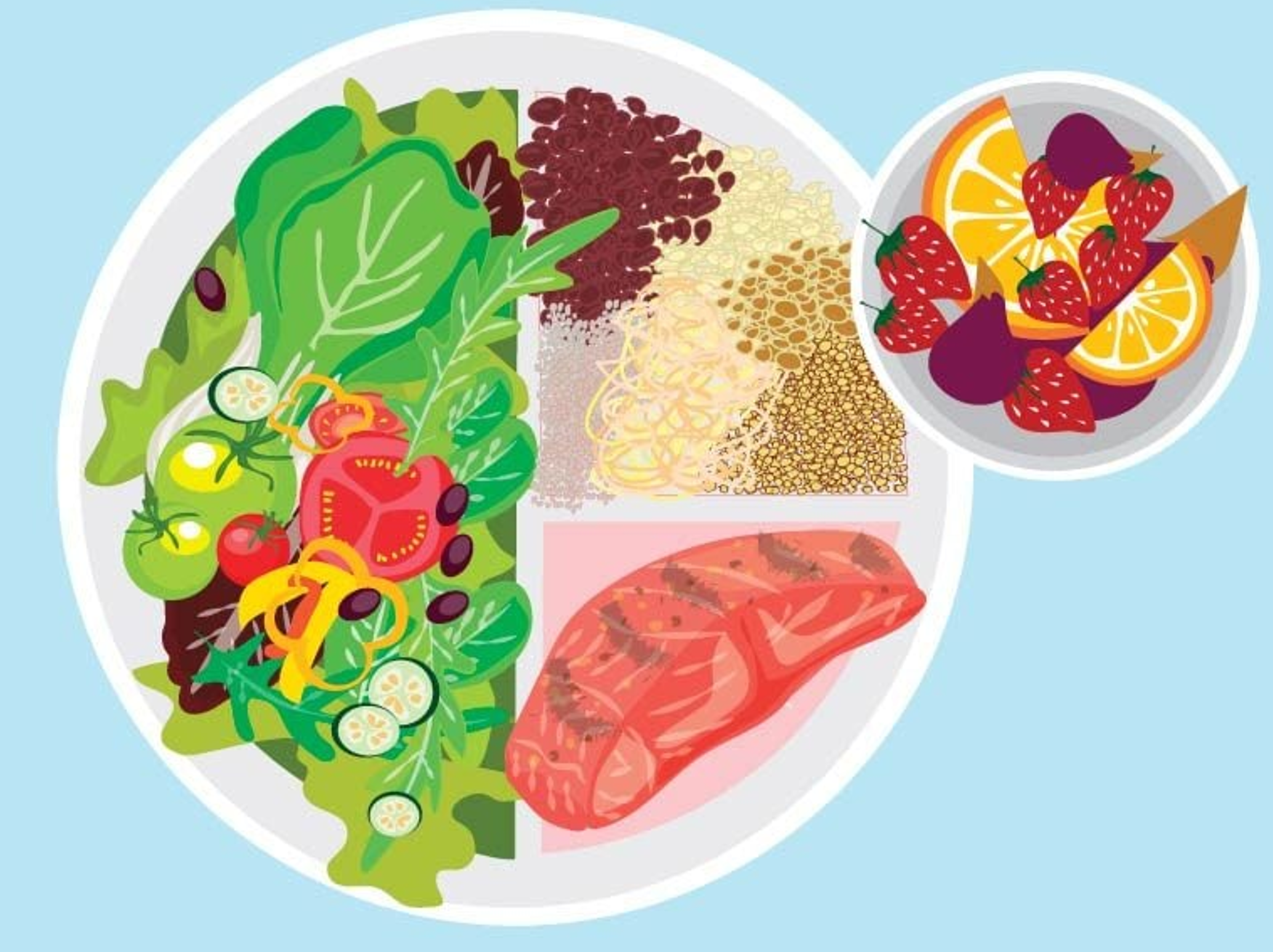
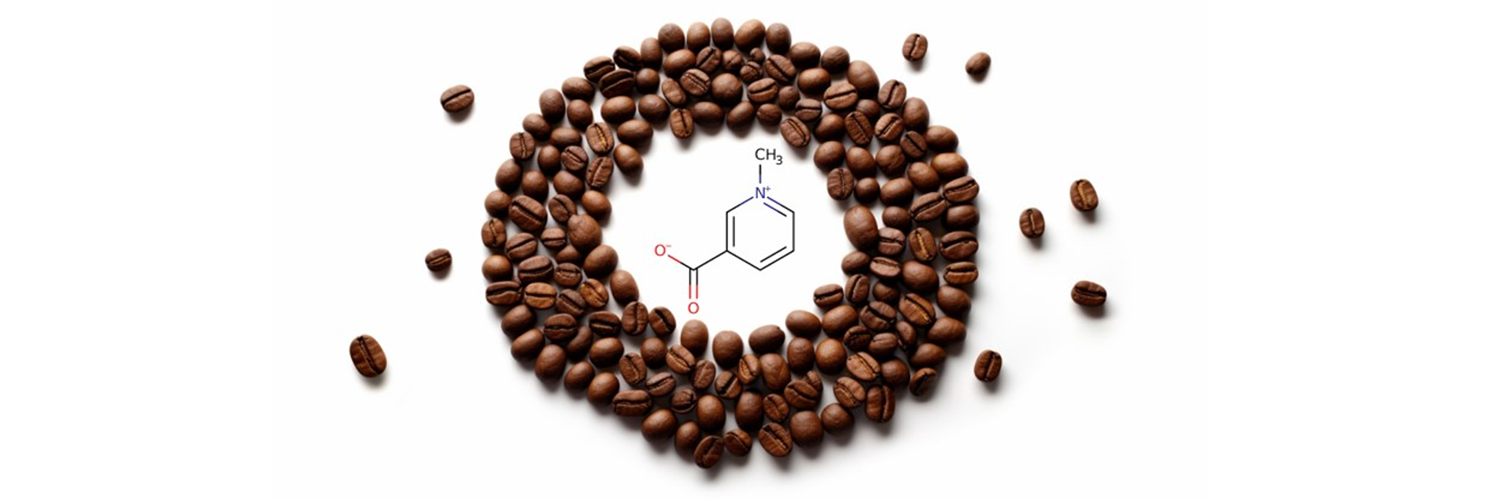
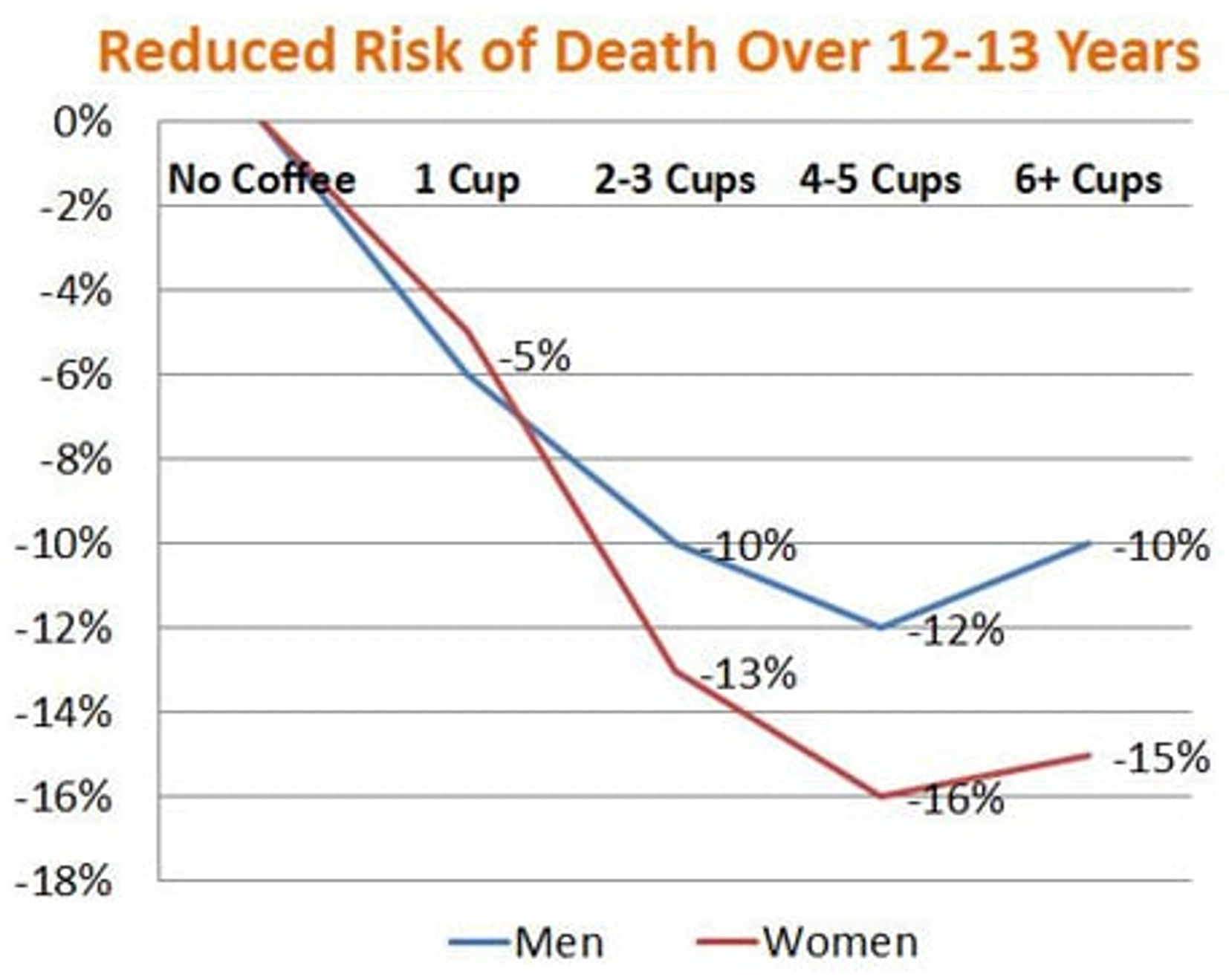

 For heart health, it champions the consumption of
For heart health, it champions the consumption of  It is not that those ingredients are bad for you, but you want to look for foods that have more healthy nutritious ingredients that add value to your body. The report also points to a burgeoning interest in traditional and
It is not that those ingredients are bad for you, but you want to look for foods that have more healthy nutritious ingredients that add value to your body. The report also points to a burgeoning interest in traditional and 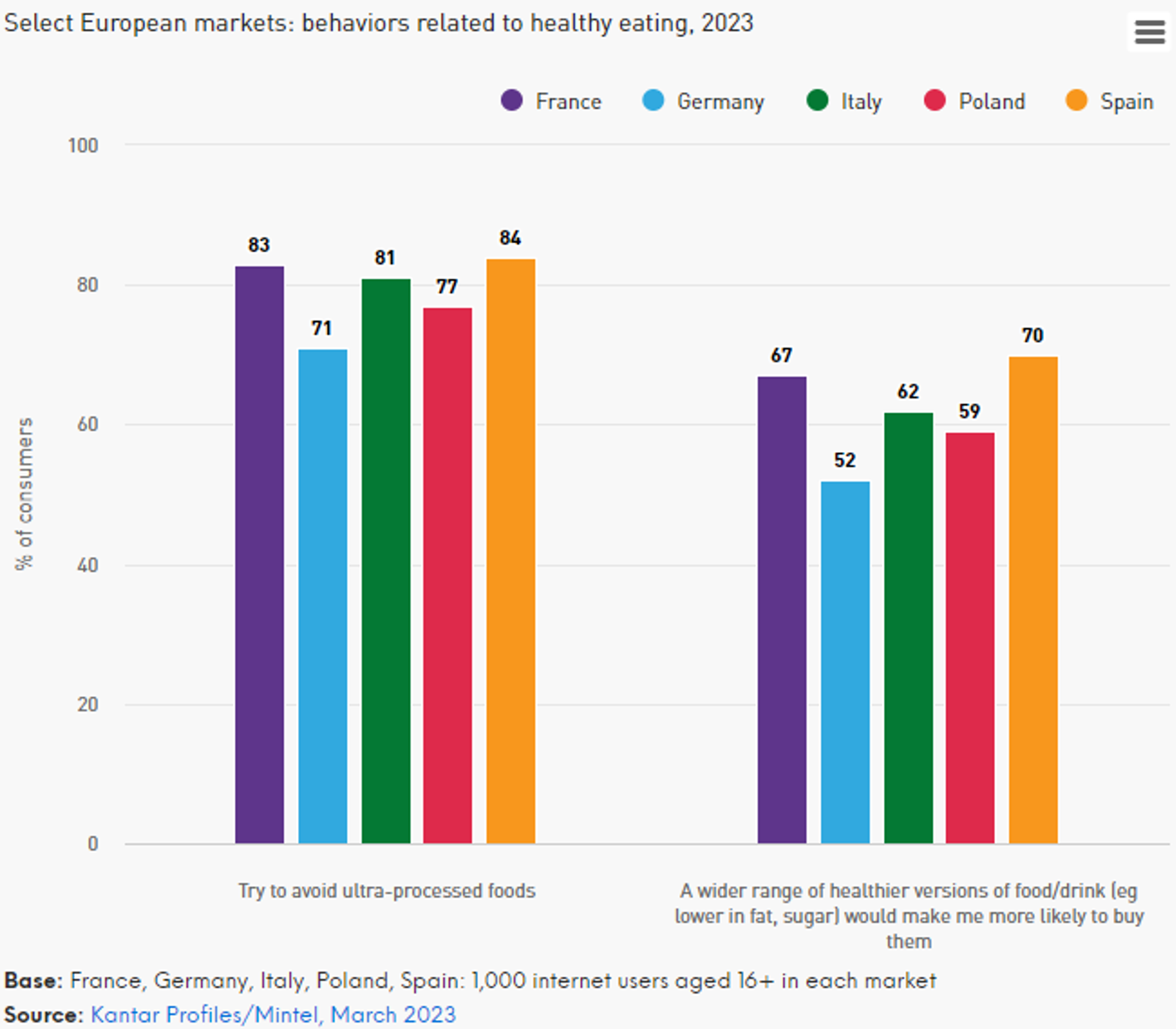




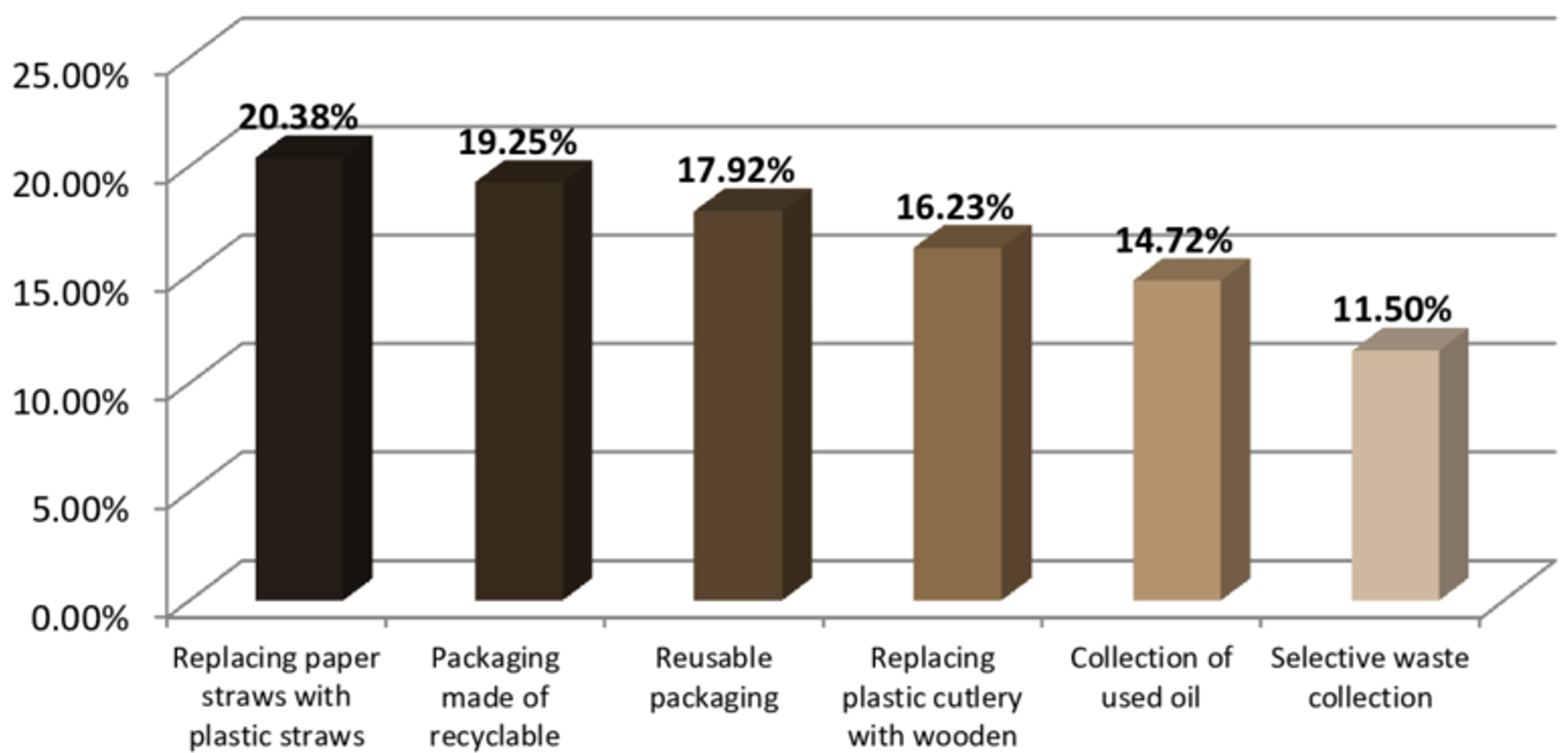
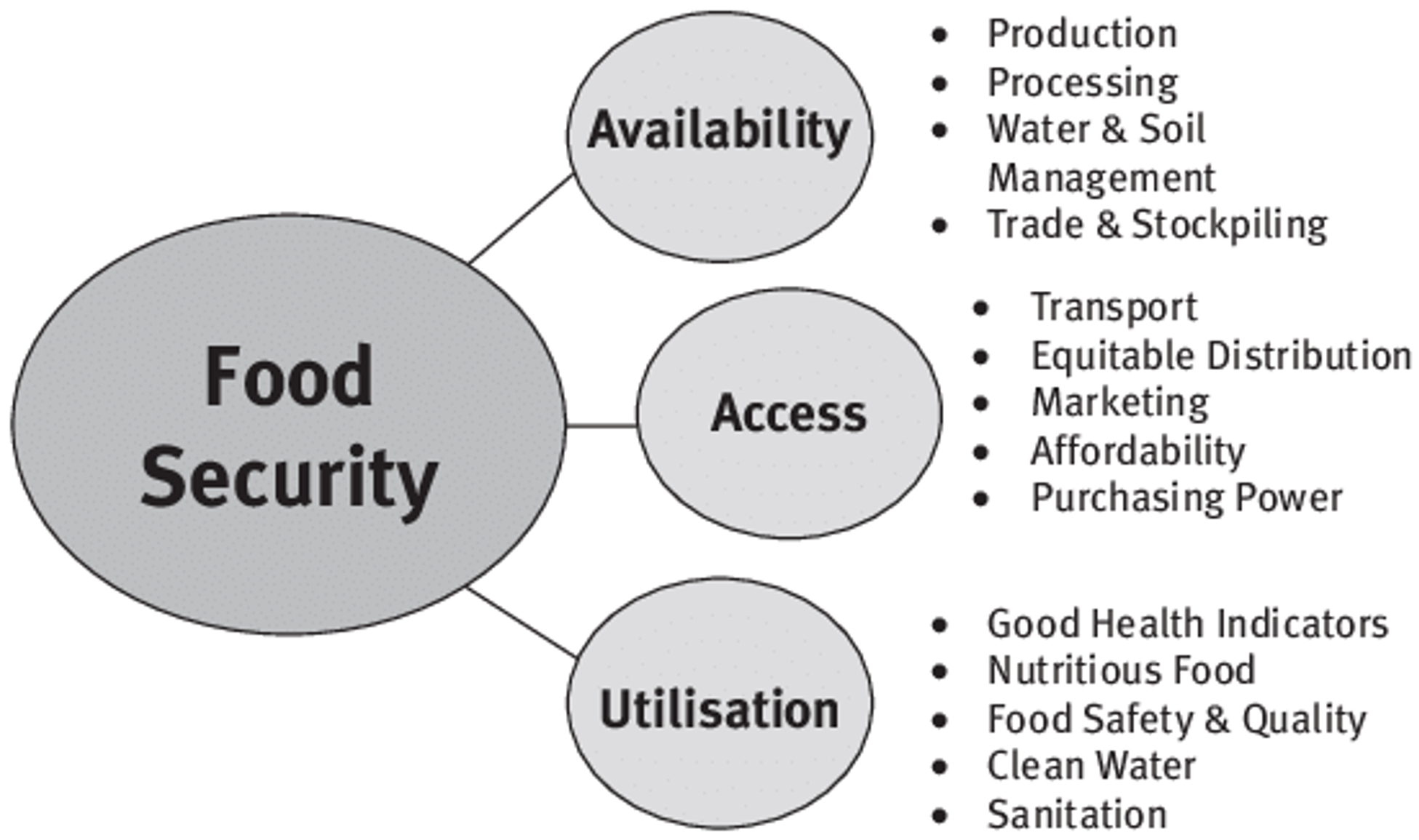
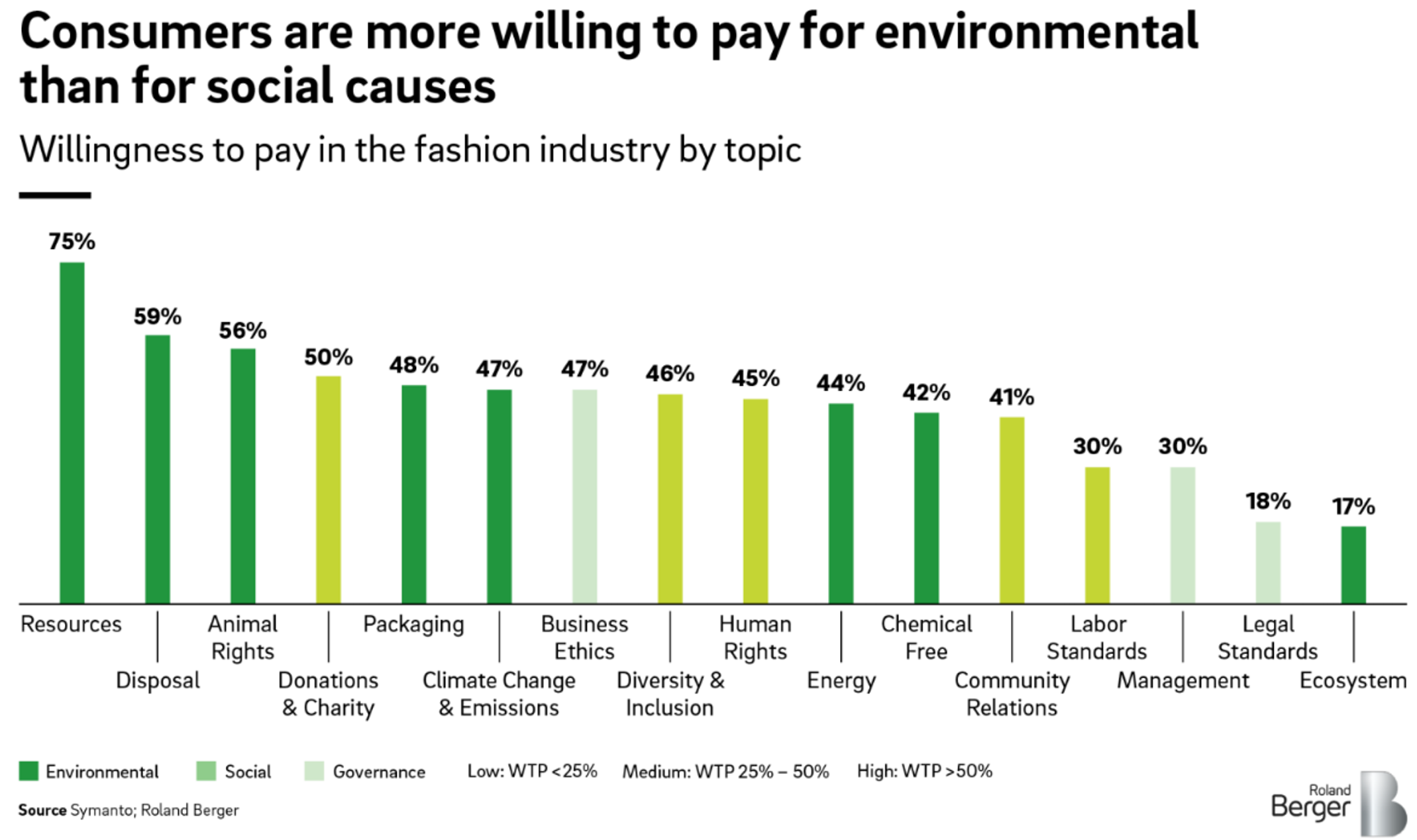


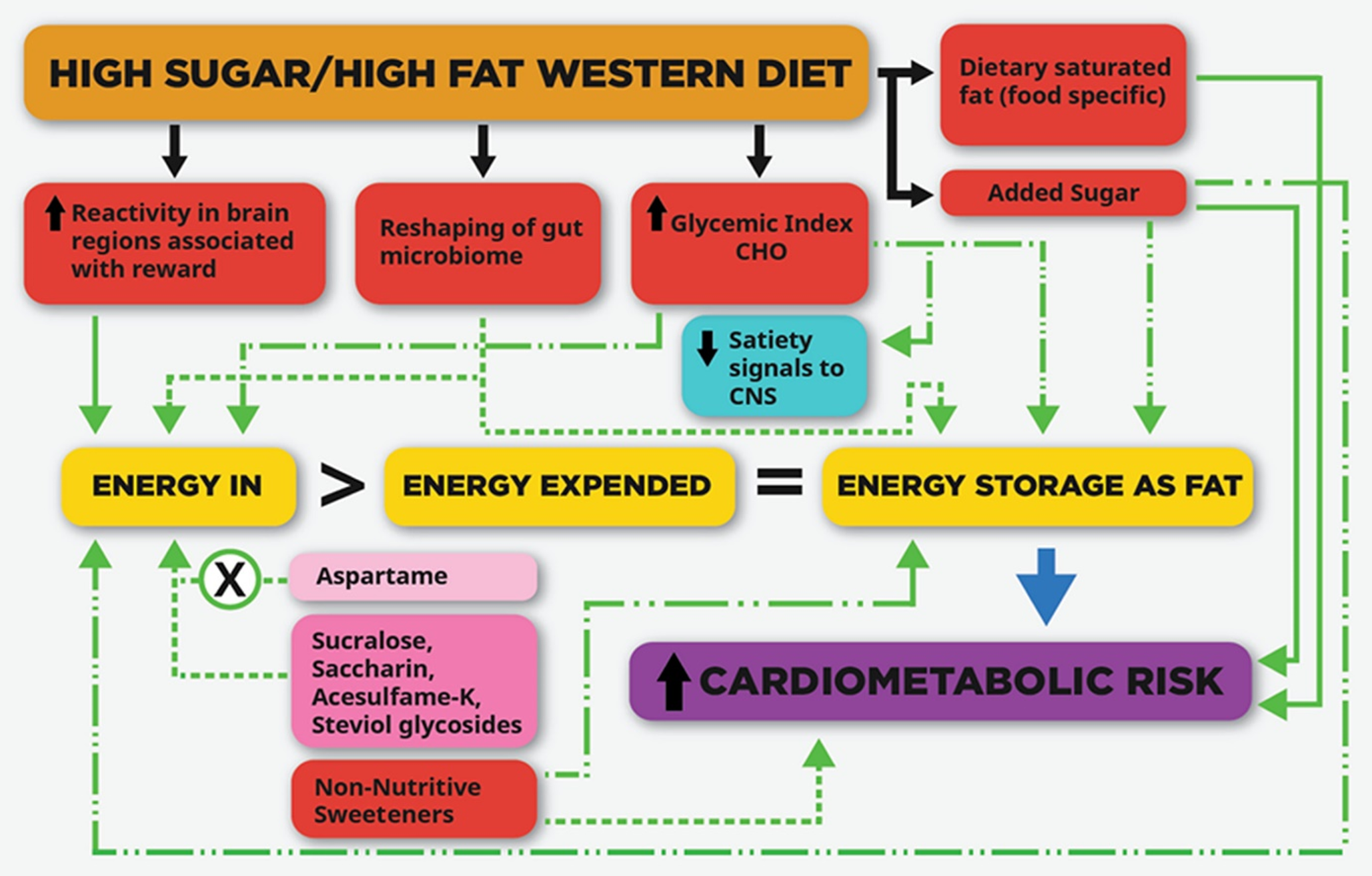


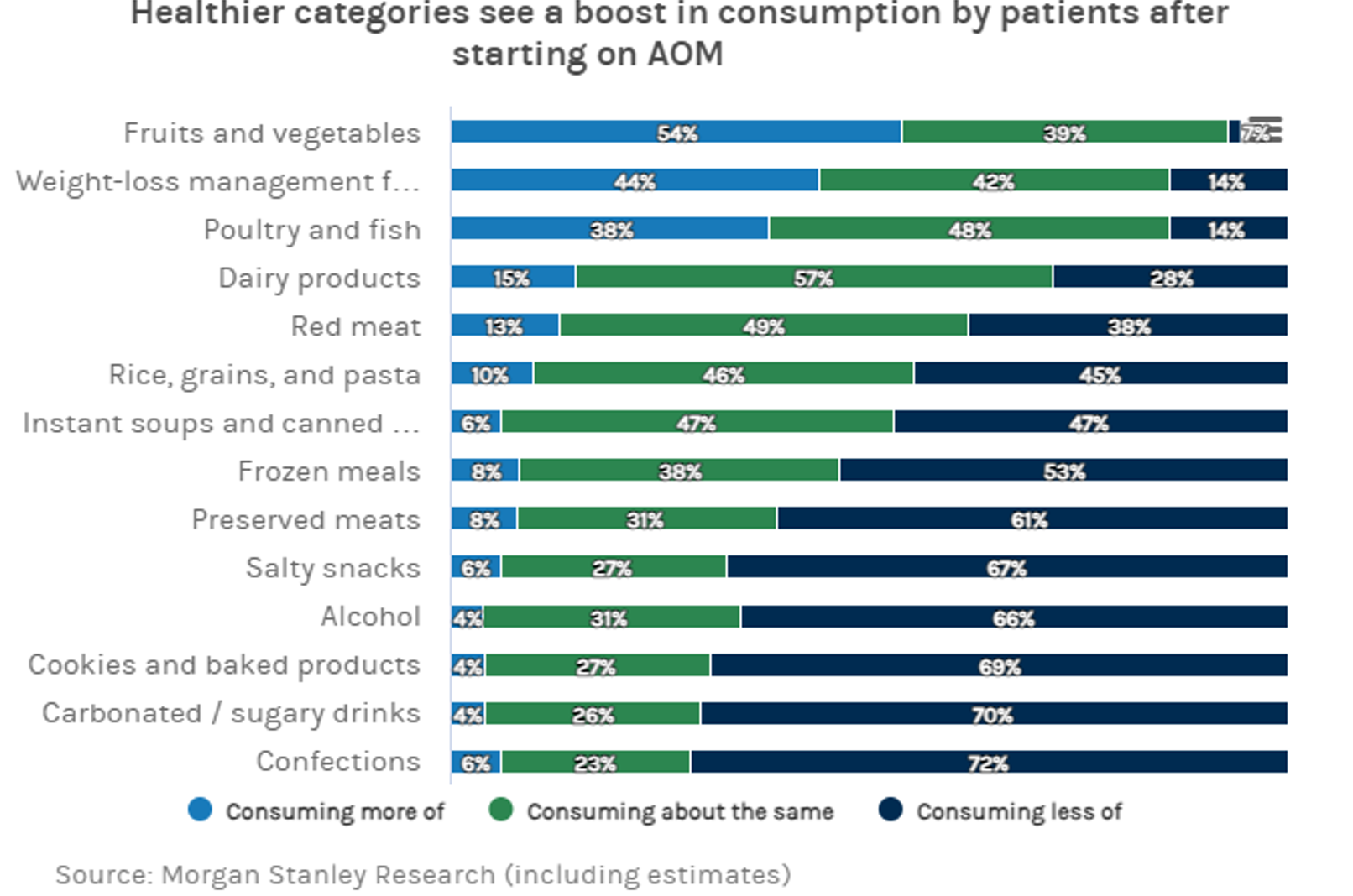
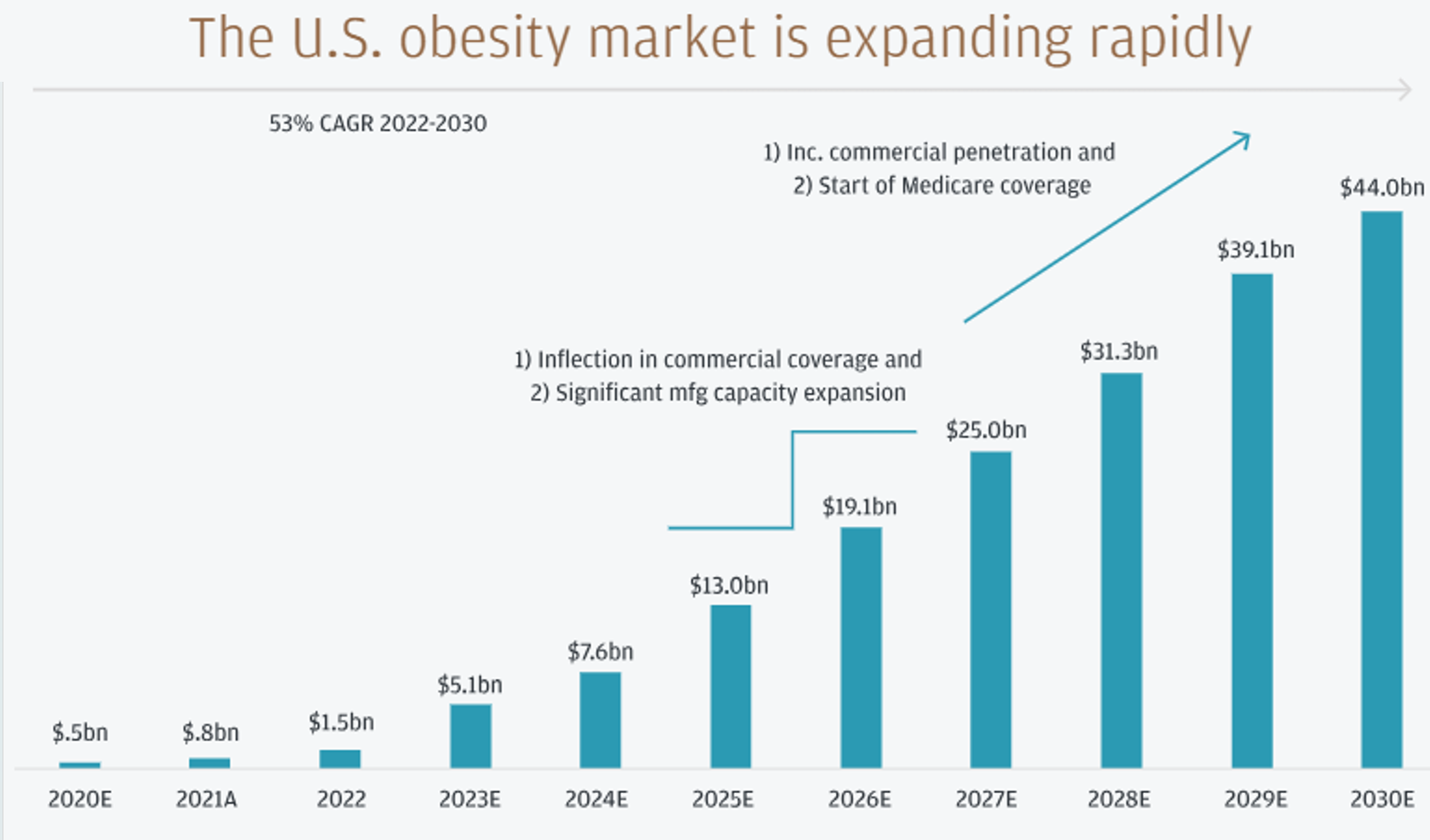




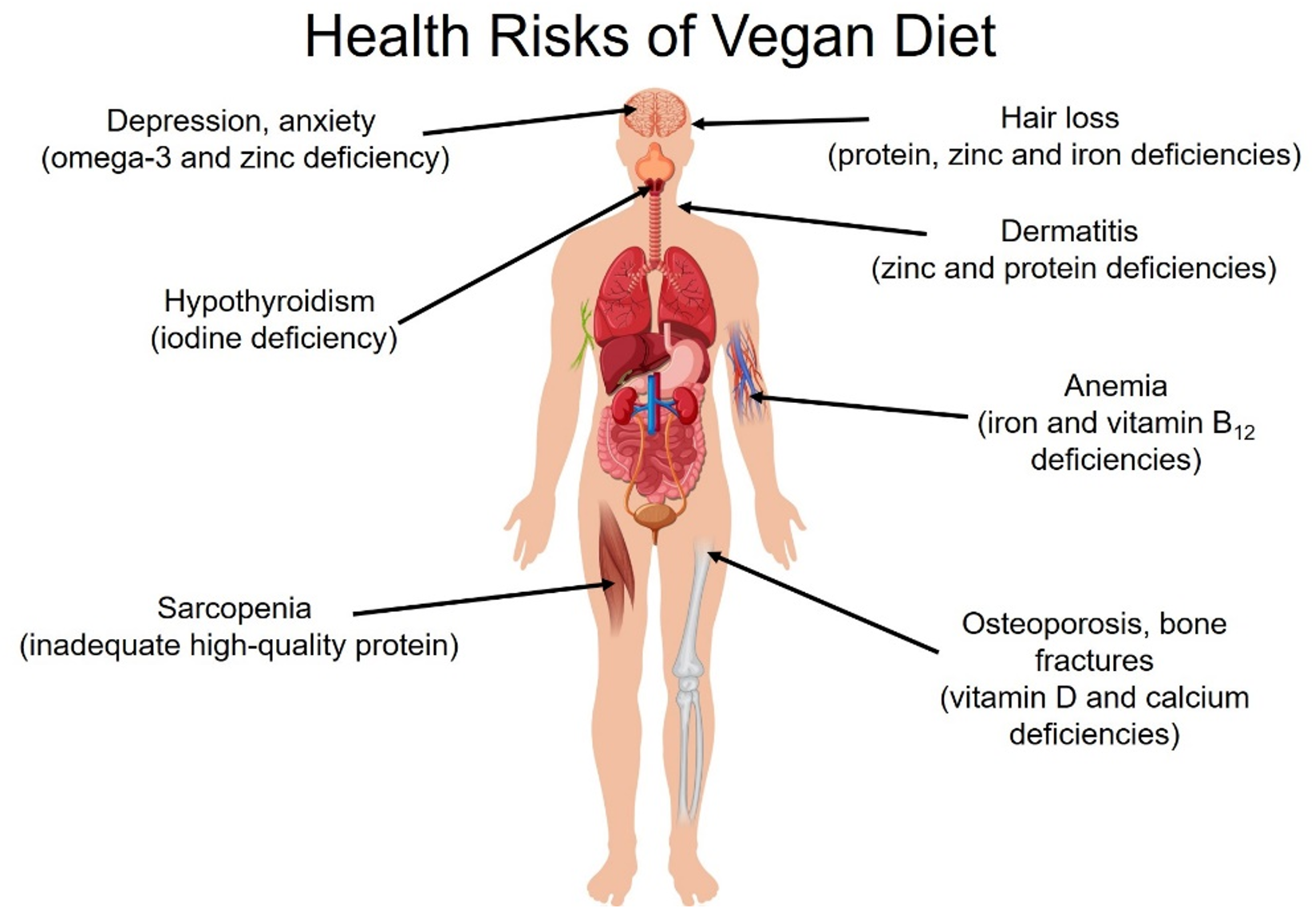


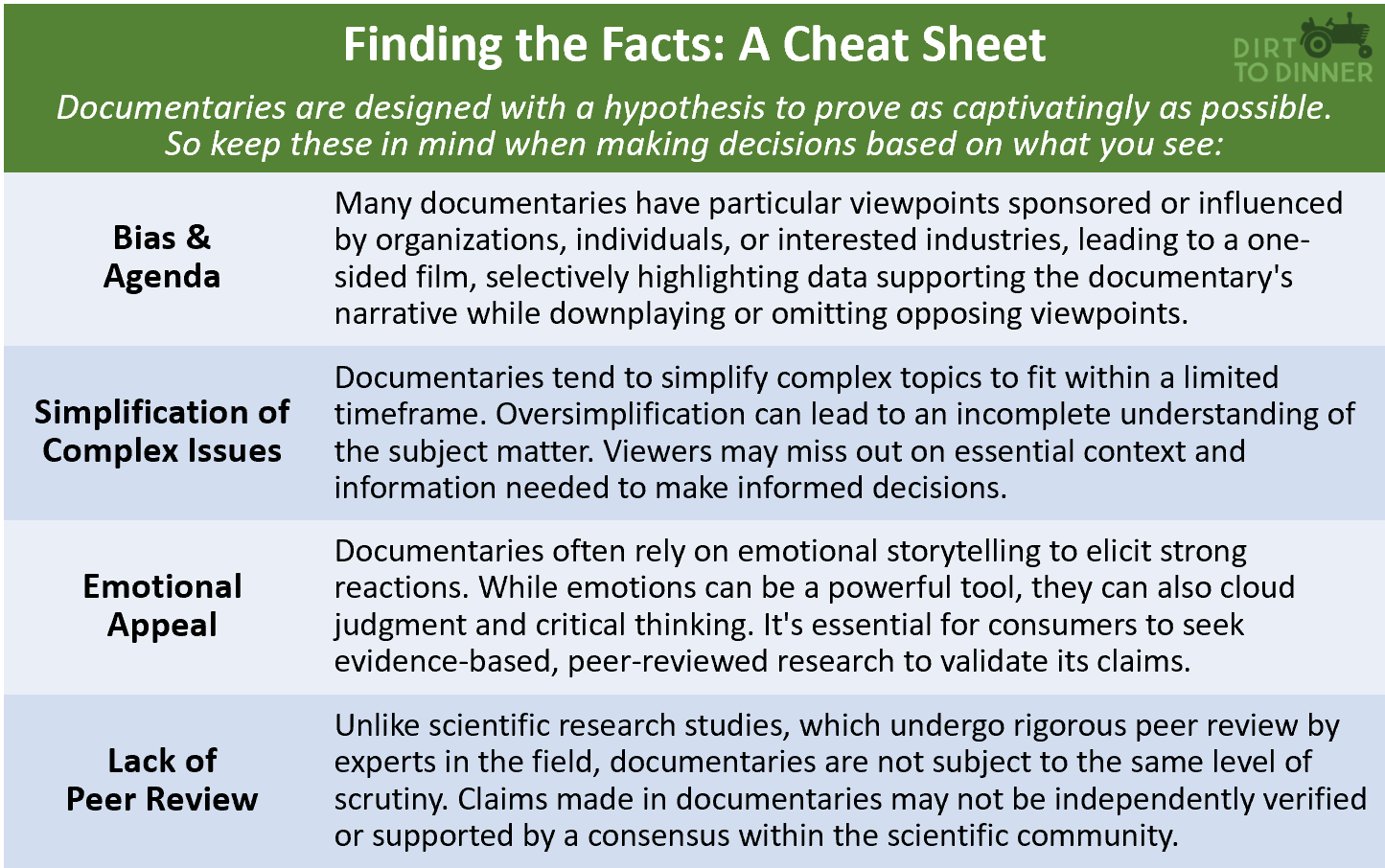

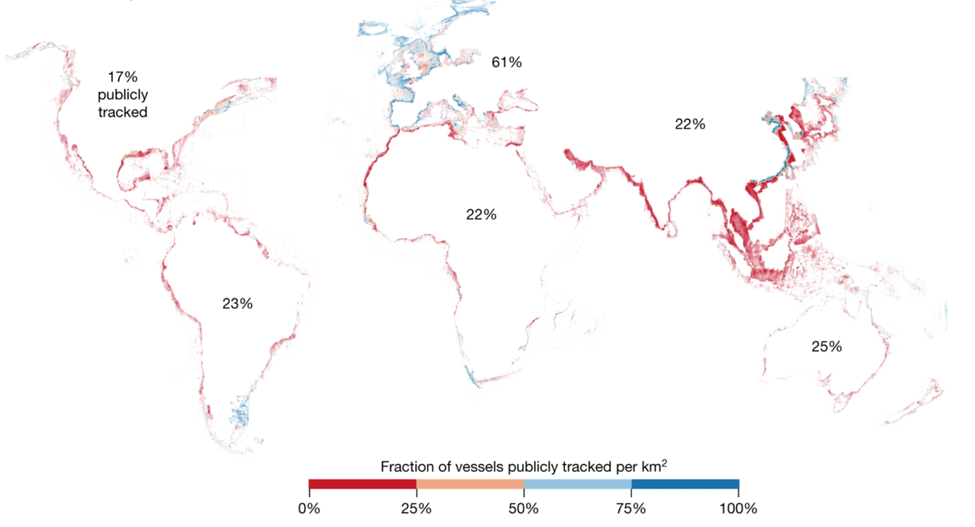
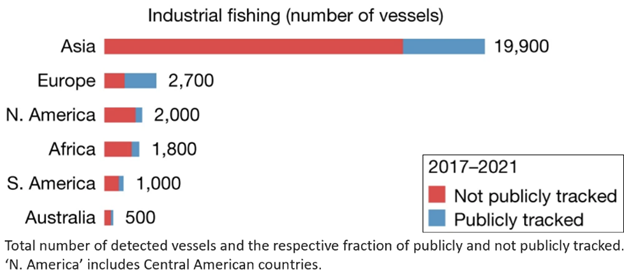
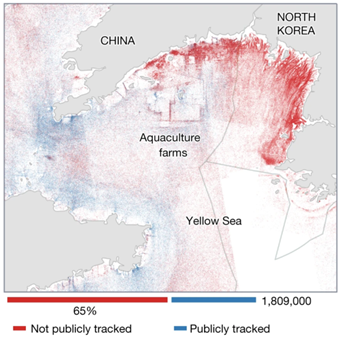
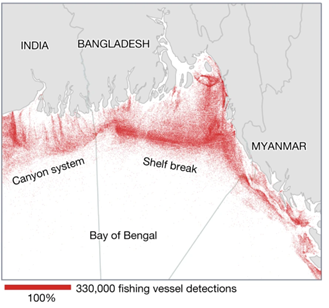







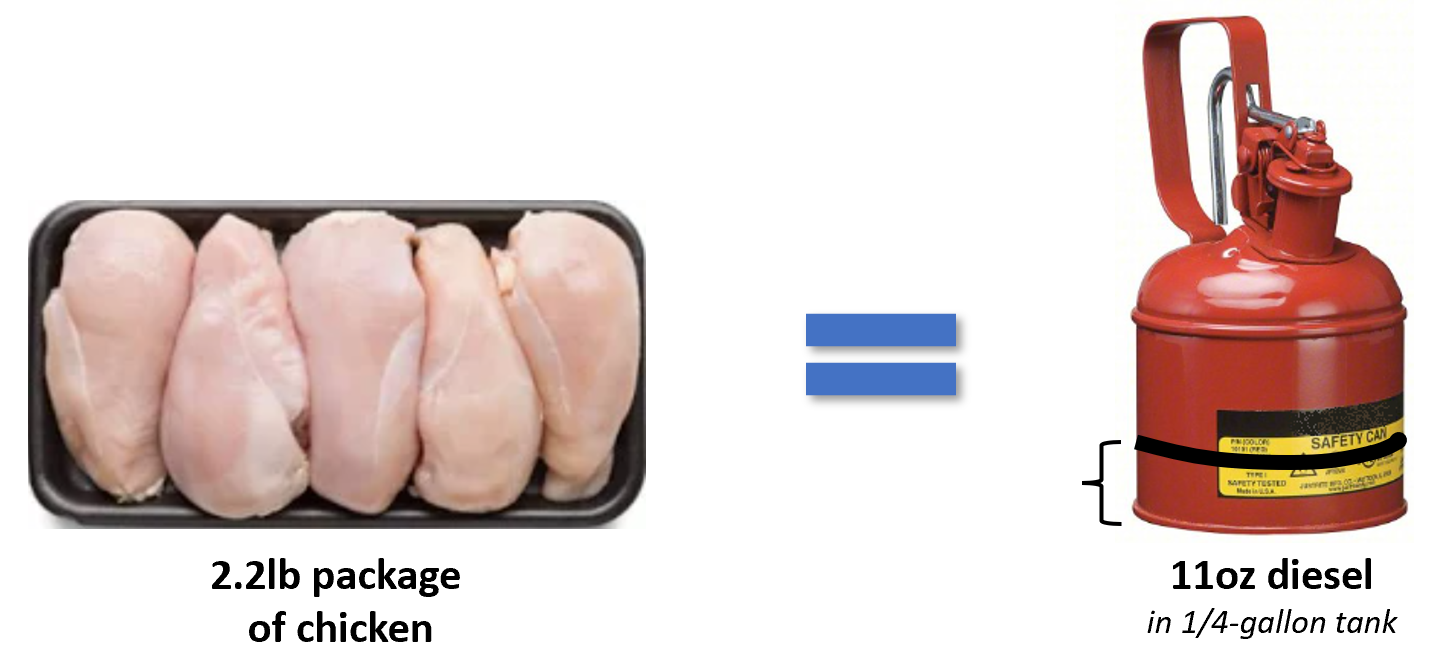






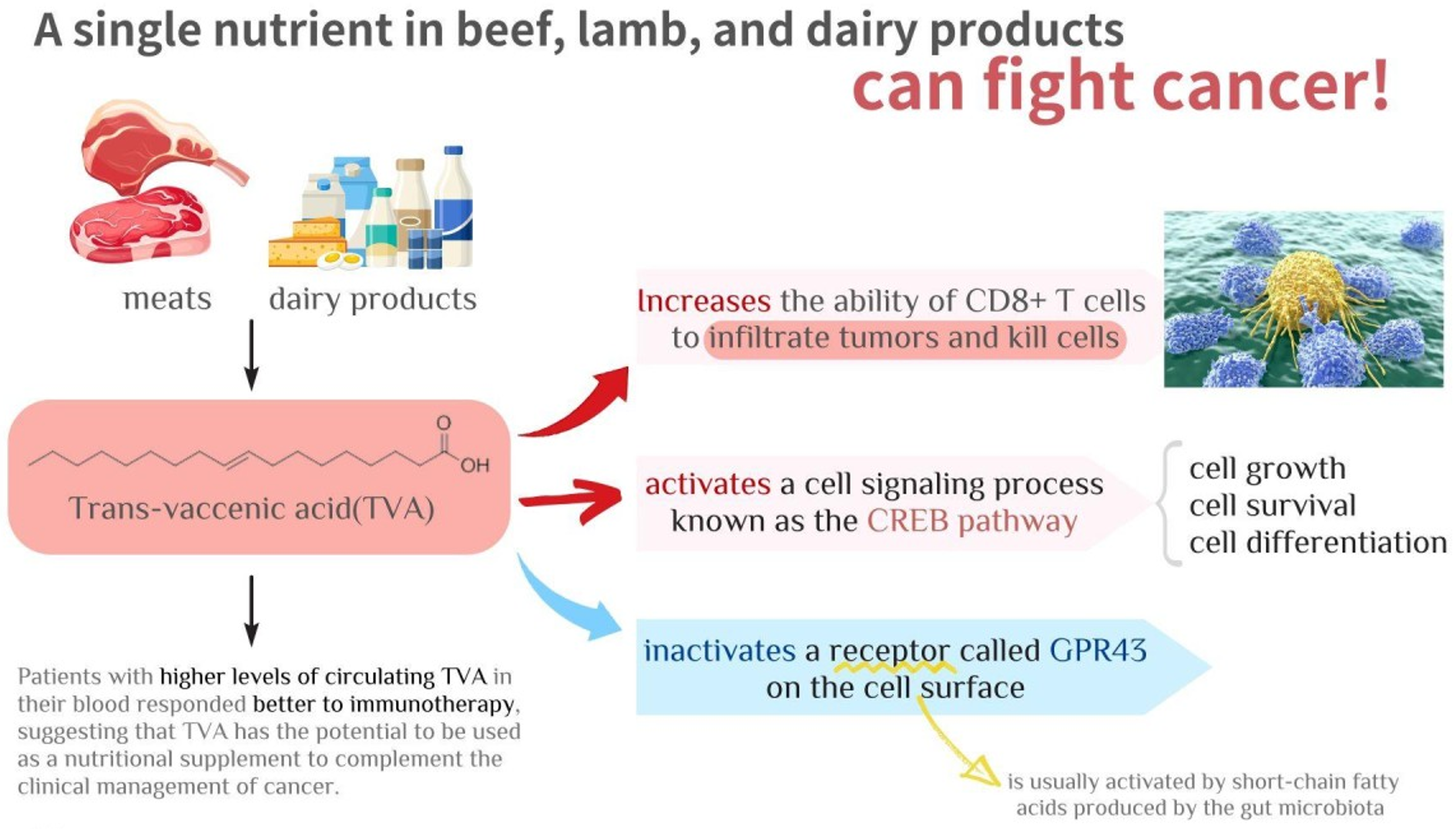
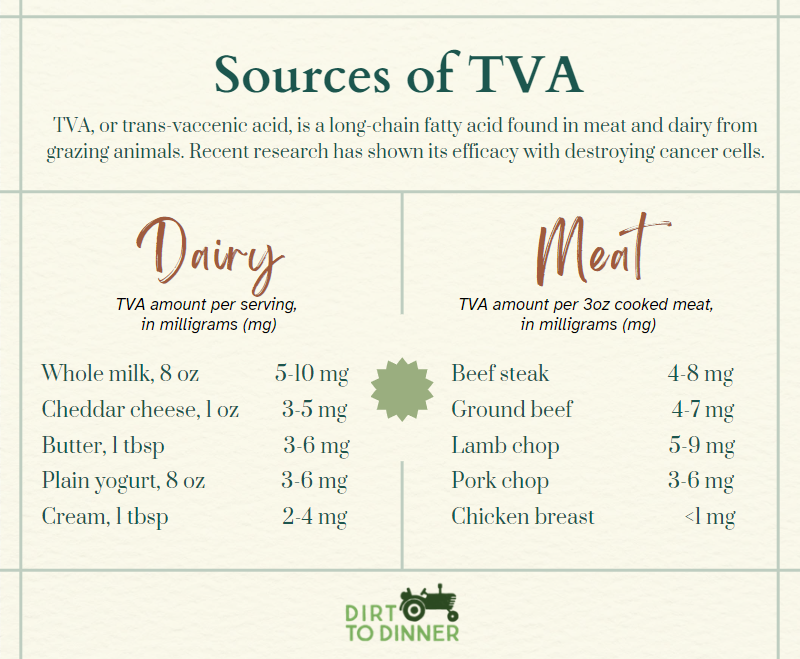





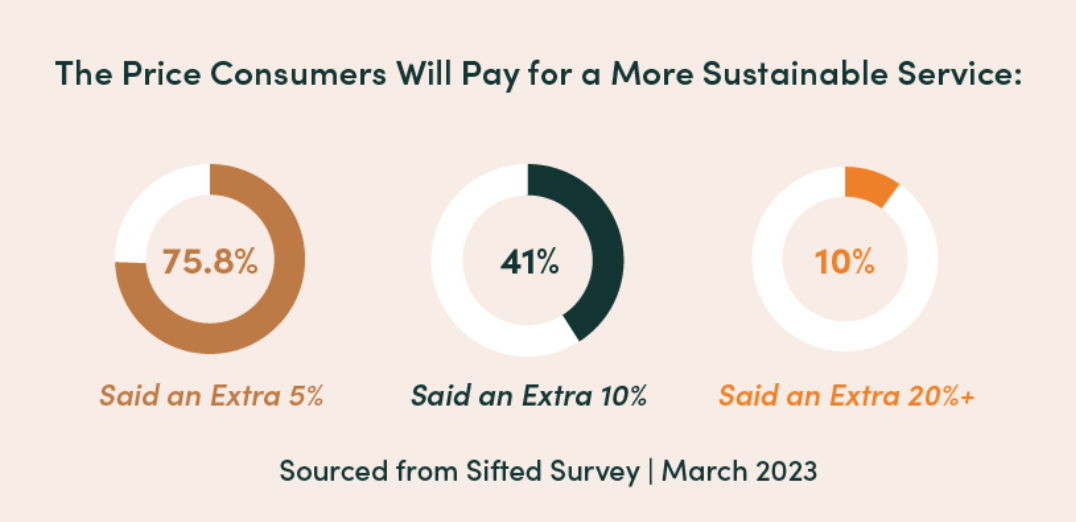

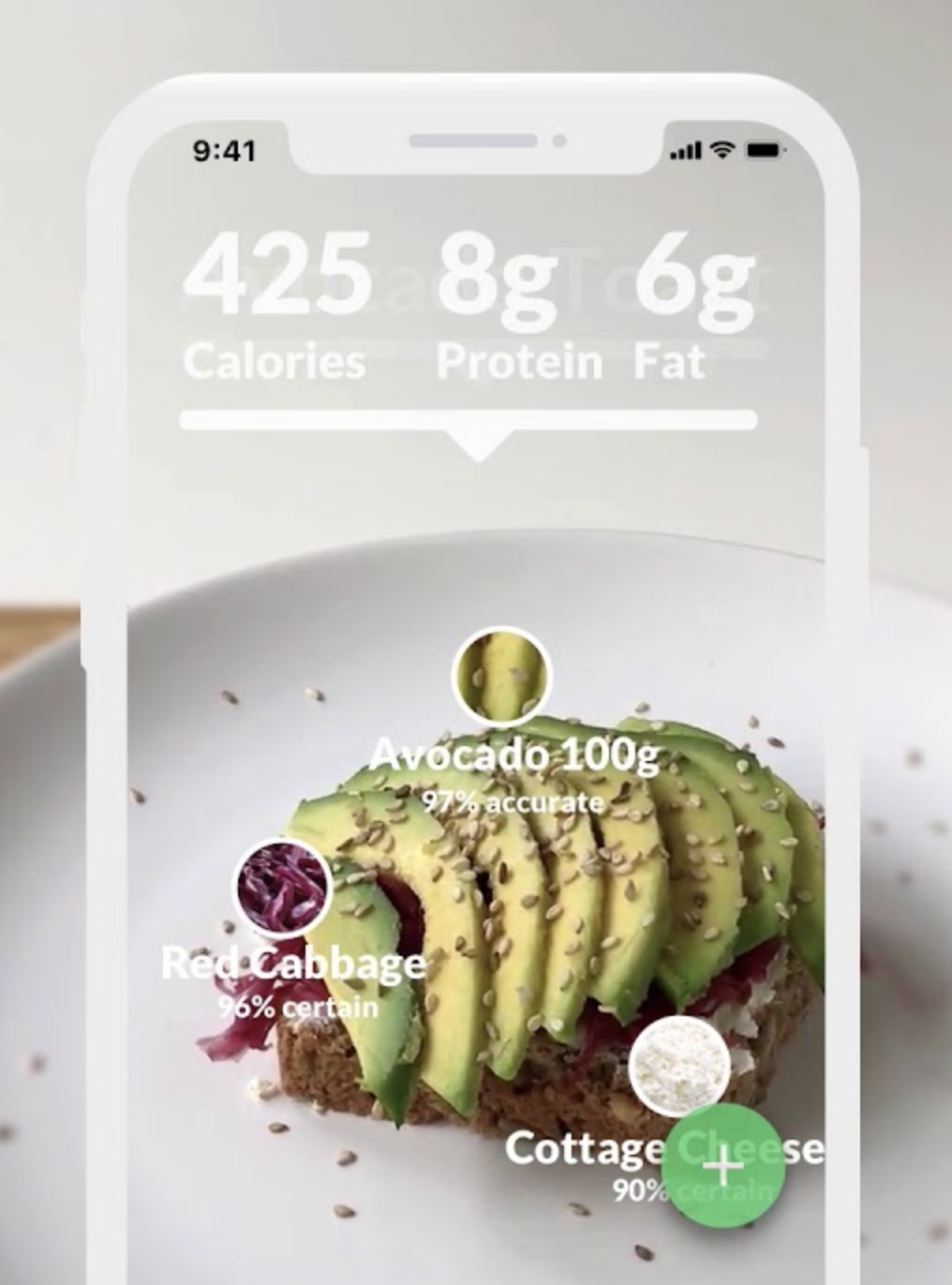






 Let’s briefly examine just some of the ways the Belief Effect impacts overall health.
Let’s briefly examine just some of the ways the Belief Effect impacts overall health.









 When a cow eats a plant, it consumes carbohydrates – which contain carbon. It swallows the plant into their four-chambered stomach. The first chamber is massive and holds enough food to fill your bathtub – about 50 gallons. After the plant enters their stomach, they bring it back up to chew some more – “chewing their cud.” The food then goes back down to the stomach to be digested by the microbes, called methanogens.
When a cow eats a plant, it consumes carbohydrates – which contain carbon. It swallows the plant into their four-chambered stomach. The first chamber is massive and holds enough food to fill your bathtub – about 50 gallons. After the plant enters their stomach, they bring it back up to chew some more – “chewing their cud.” The food then goes back down to the stomach to be digested by the microbes, called methanogens.














 Consider pairing this cheesecake with a
Consider pairing this cheesecake with a 












 No labor shortage provides greater cause for concern than the trucking sector.
No labor shortage provides greater cause for concern than the trucking sector.











 Good news for you, most people already consume more than double the recommended amount, typically 900-1000 milligrams daily as part of their regular diets. Some tryptophan-dense foods are cod, spirulina, nuts and seeds, and legumes.
Good news for you, most people already consume more than double the recommended amount, typically 900-1000 milligrams daily as part of their regular diets. Some tryptophan-dense foods are cod, spirulina, nuts and seeds, and legumes. Not sure how to tell the difference between a complex carb and a simple carb? Here’s a good trick: most whole, unprocessed foods contain complex carbs. Avoid processed foods and “white” foods, which are mostly comprised of simple carbs.
Not sure how to tell the difference between a complex carb and a simple carb? Here’s a good trick: most whole, unprocessed foods contain complex carbs. Avoid processed foods and “white” foods, which are mostly comprised of simple carbs.















 Wildfire smoke is a devil’s brew of harmful ingredients – carbon monoxide, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, water vapor and various particulate matters. As fires burn, these substances rise in the air, driven upward by heat, finding prevailing winds aloft capable of carrying them thousands of miles.
Wildfire smoke is a devil’s brew of harmful ingredients – carbon monoxide, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, water vapor and various particulate matters. As fires burn, these substances rise in the air, driven upward by heat, finding prevailing winds aloft capable of carrying them thousands of miles. The scientific community continues to explore the question of the relationship between exposure and lasting health damage.
The scientific community continues to explore the question of the relationship between exposure and lasting health damage.

