Brewing Longevity: Coffee’s Health Benefits
The Dirt
Recent research highlights coffee's health benefits, particularly from trigonelline, which improves muscle health and has neuroprotective effects. Find out more truths and myths about coffee through the latest research.
Nutrition
Brewing Longevity: Coffee’s Health Benefits
The Dirt
Recent research highlights coffee's health benefits, particularly from trigonelline, which improves muscle health and has neuroprotective effects. Find out more truths and myths about coffee through the latest research.
Coffee gives us a great morning boost – and it is not just the caffeine! A recent study published in Nature Metabolism brings to light the significant role of trigonelline, a naturally occurring compound in coffee, in enhancing muscle health and function, particularly against the backdrop of aging.
Trigonelline is an alkaloid that serves as a precursor to NAD+. This molecule is crucial for energy production in cells, particularly within mitochondria — the powerhouses of cells.
New Research on Trigonelline
As we age, our mitochondria’s efficiency in energy production wanes, partly due to declining NAD+ levels. This decline is linked to several age-related conditions, including sarcopenia, which is characterized by the loss of skeletal muscle mass and strength.
Think of trigonelline in the body like a key that unlocks the energy production factory in muscle cells. Just as a key starts a car and revs the engine, trigonelline helps turn on the mitochondria, boosting energy output and enhancing muscle function, especially as we age. This ensures the body’s engines run smoothly and efficiently.
These effects were observed across various species, including humans, where higher blood levels of trigonelline were positively correlated with better muscle strength and function.
Conversely, lower levels were associated with sarcopenia, or muscle loss.
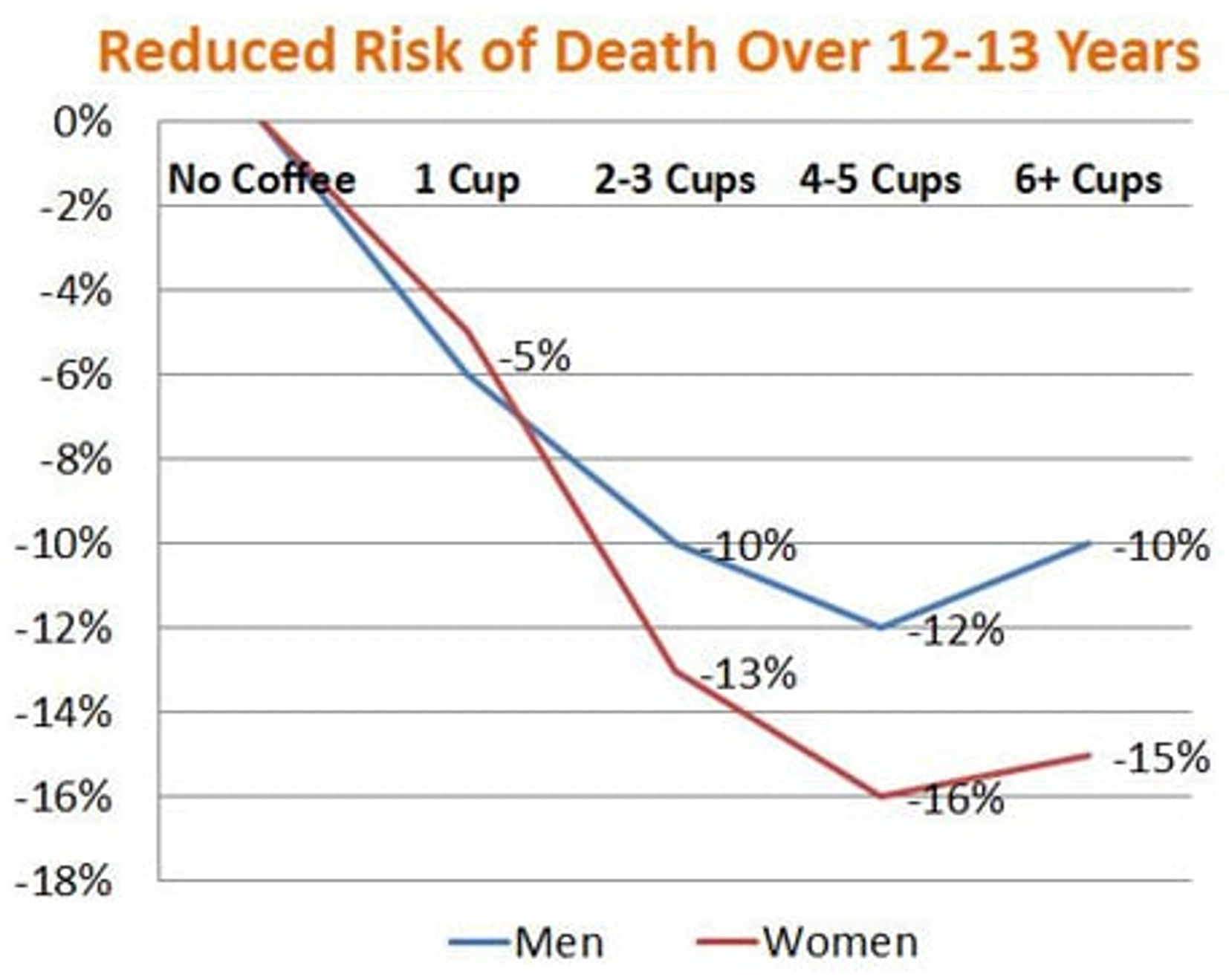
The implications of these findings are vast.
For one, it suggests that daily consumption of coffee, a rich source of trigonelline, could offer a simple, natural way to support muscle health and mitigate some aspects of aging.
The study, however, does not specify the exact amount of coffee required to achieve these benefits, as trigonelline content can vary widely among different coffee types and preparations.
Generally, a moderate intake of black coffee (approximately 3-4 cups per day) is considered beneficial for most people, but individual responses can vary.
Debunking Myths
But what about coffee’s negative effects? Does the trigonelline make up enough for them?
First, let’s dispel some of these outdated coffee myths:
⊗ Coffee causes dehydration
- While caffeine has a mild diuretic effect, the fluid content in coffee helps to maintain hydration levels. Studies suggest that for regular coffee drinkers, this diuretic effect is minimal.
⊗ It causes heart disease
- Numerous studies have shown that moderate coffee consumption does not increase the risk of heart disease. In fact, some research indicates that it may have protective effects against certain cardiovascular issues.
⊗ It’s addictive
- While caffeine can be mildly habit-forming, it does not stimulate the brain’s reward circuitry in the same way as addictive drugs. Most people can manage or reduce coffee consumption without the severe withdrawal symptoms associated with true addiction.
⊗ It stunts growth
- Scientific evidence does not support the idea that coffee consumption affects growth. This myth may have originated from the misconception that coffee causes osteoporosis, which it does not when consumed in moderation.
⊗ It causes cancer
- In 2016, the World Health Organization moved coffee off its “possible carcinogen” list, acknowledging the lack of evidence that coffee causes cancer. Some studies suggest that coffee may even reduce the risk of certain types of cancer.
Coffee Health Facts
And there are plenty of other reasons to enjoy your cup of joe, in addition to minimizing muscle loss.
♥ Antioxidants
- In addition to trigonelline, coffee is rich in powerful antioxidants, like chlorogenic acid and caffeine, which can neutralize harmful free radicals. This antioxidant activity is linked to a reduced risk of diseases such as heart disease and certain cancers.
♥ Caffeine
- As the most well-known active ingredient in coffee, caffeine has been studied extensively. It’s known to enhance brain function, improve mood, and boost metabolism. A study published in “The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition” suggests that caffeine can increase metabolic rate by up to 11% and enhance physical performance.
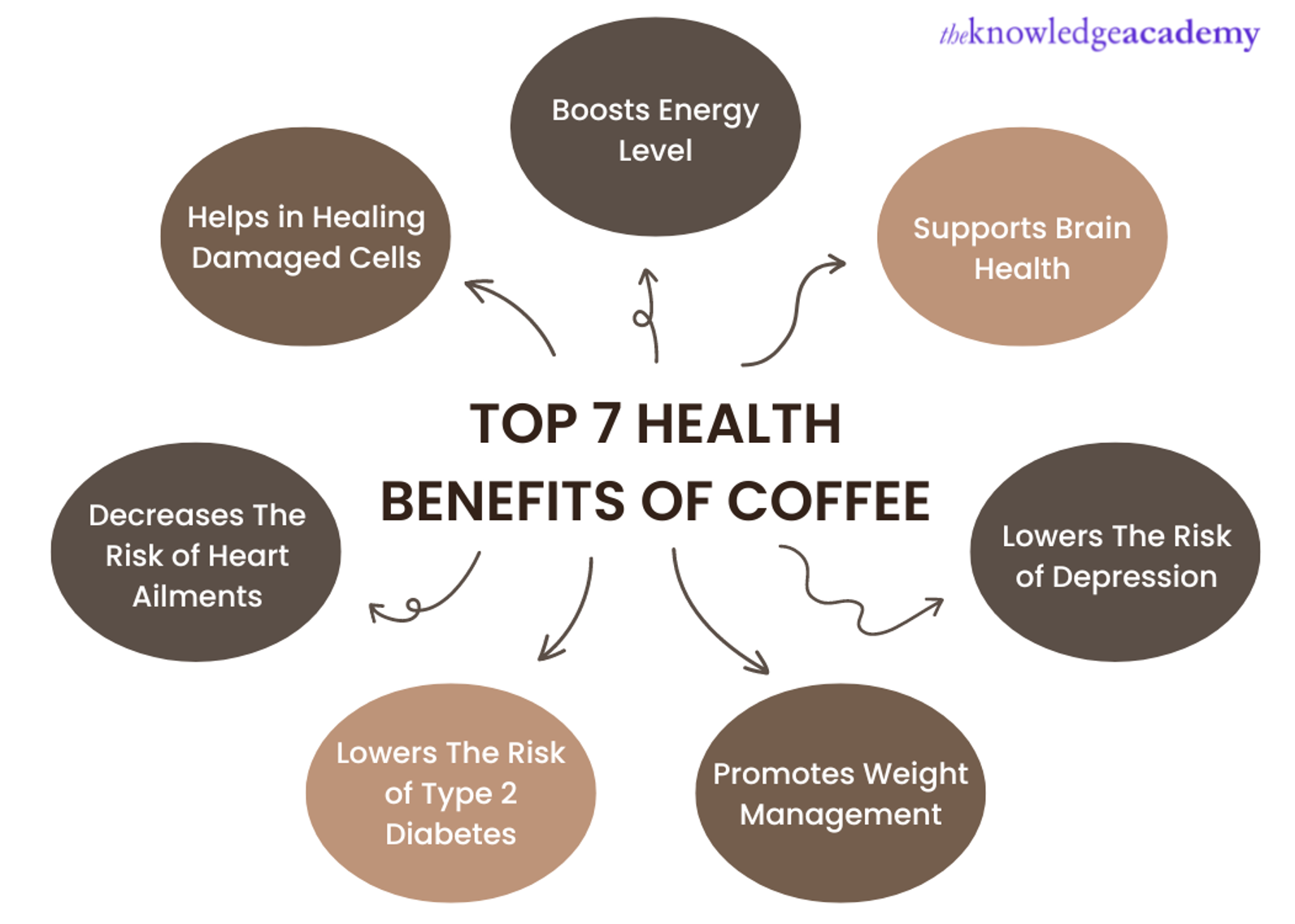
♥ Chlorogenic Acid
- This is another significant component, believed to help lower blood sugar levels and potentially reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes. A study in “The Journal of Nutrition” found that chlorogenic acid might improve glucose metabolism, which is crucial for managing diabetes.
♥ Magnesium & B Vitamins
- Coffee contains essential nutrients, including magnesium and B vitamins, which play crucial roles in numerous bodily functions, including energy metabolism and DNA repair.
It’s also worth noting that while coffee’s potential health benefits are promising, it’s important to consume it in moderation and be mindful of individual tolerance levels. Additionally, the healthiest way to enjoy coffee is black, or with minimal added sugar, to avoid counteracting its benefits with unnecessary calories.
This study, a collaboration among international researchers, underscores the potential of dietary interventions to improve health outcomes, especially in aging populations. It opens doors to further research on trigonelline’s role in human health and its potential in dietary supplements or as part of a broader strategy to combat age-related muscle decline.
Reputable Sources for Food Info
How do these myths and truths come to exist in people’s minds? It is all about the source.
In the landscape of nutrition and health information, the importance of consulting reputable sources cannot be overstated.
These sources, like Dirt to Dinner, are grounded in scientific research and peer-reviewed studies, and offer reliable and evidence-based insights, ensuring the advice you follow is beneficial for your health. They help sift through myriad information available, distinguishing between evidence-based facts and unfounded claims to help eliminate unfounded myths such as these.
This careful approach to gathering information is essential for making informed decisions about your diet and health, contributing to a well-rounded understanding of nutrition’s role in overall well-being and helping to navigate through common myths and misconceptions.
The Bottom Line
Daily consumption of coffee, a rich source of trigonelline, could offer a simple, natural way to support muscle health and mitigate some aspects of aging, among other benefits. Many myths and truths exist not only about coffee but all sorts of foods. Be sure to seek reputable sources when it comes to information on your food!







